The electrical system is the “backbone” of any industrial factory. From production lines, HVAC systems, air compressors to every office device, all operations rely on an electrical system that is accurately designed, properly installed, and thoroughly tested before operation. With experience in implementing large-scale FDI projects such as Dainese Vietnam, Haem Vina, GS Binh Duong, Power Plus Technology, Dorco Ha Nam…, DELCO has a comprehensive perspective on how to build a safe, stable electrical system that meets the factory’s long-term development goals.

1. Main items of factory electrical systems
1.1. Medium–low voltage system and power supply design
- Electrical design plays a pivotal role in ensuring safety, stability, and operational cost control of a factory. The design process must determine total load, allocate loads by zone, arrange backup power sources, and forecast expansion needs for five to ten years. The system must comply with TCVN 7447 (equivalent to IEC 60364) to ensure safe, efficient, and cost-effective operation.
- Core calculations:
Include short-circuit calculations (for selecting breaking capacity), voltage drop calculations (for cable sizing), and selectivity/coordination settings for protection systems (MCCB/ACB/relay). - Backup power source:
ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) enables automatic switching between the grid and generators, minimizing downtime and ensuring safety for high-capacity equipment. - For critical loads requiring uninterrupted power, UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) or STS (Static Transfer Switch) should be used.
- All above components must comply with QCVN 01:2020/BCT on electrical safety.

Medium voltage cabinets arranged with two compartments and space reserved for capacity expansion in a printing factory.
1.2. Substation layout and electrical cabinet configuration
The layout and design of main equipment must comply with the highest technical standards.
The substation, medium voltage, and low voltage cabinets (MSB) must follow current standards (QCVN 01:2020/BCT on electrical safety, TCVN 394:2007 on substation safety, fire safety standards in QCVN 02:2020/BCA and QCVN 06:2022/BXD…), ensuring safety clearances, ventilation, fire protection, and maintenance access.
Cabinet standards: Low voltage cabinets must comply with IEC 61439 (switchgear assemblies) and IEC 60947 (electrical devices).
Structure: Apply functional compartmentalization (busbar compartment, equipment compartment, cable compartment) for enhanced safety. Equipment is arranged according to a Single-Line Diagram (SLD), with reserved space and optimized operation pathways.
1.3. Earthing and lightning protection systems
Earthing:
Earthing design follows TCVN 4756 and TCVN 7447-4-41, including safety earthing for equipment and technical earthing for sensitive systems.
Lightning Protection:
Design includes both direct lightning protection (lightning rods or Faraday cages) and surge protection (SPD – Surge Protection Device) per TCVN 9385:2012/IEC 61643, installed in main switchboards.
1.4. Lighting and socket outlet design
Lighting: Illuminance is calculated per TCVN 3890:2023 and TCVN 7114-1:2008 for each zone. Includes task lighting, maintenance lighting, emergency lighting, and exit signs.
Socket outlets: Industrial and maintenance outlets arranged with IP ratings suitable for the working environment.
1.5. Extra Low Voltage (ELV) system design
For modern factories, the following ELV systems must be synchronously designed:
Fire Alarm System (FAS): Design fire zones, smoke/heat detectors per fire protection standards, ensuring compliance with TCVN 5738.
Security and Surveillance: CCTV cameras and Access Control systems.
Information Systems: Computer network infrastructure (Data), telephone (Telecom), and public address (PA) systems.
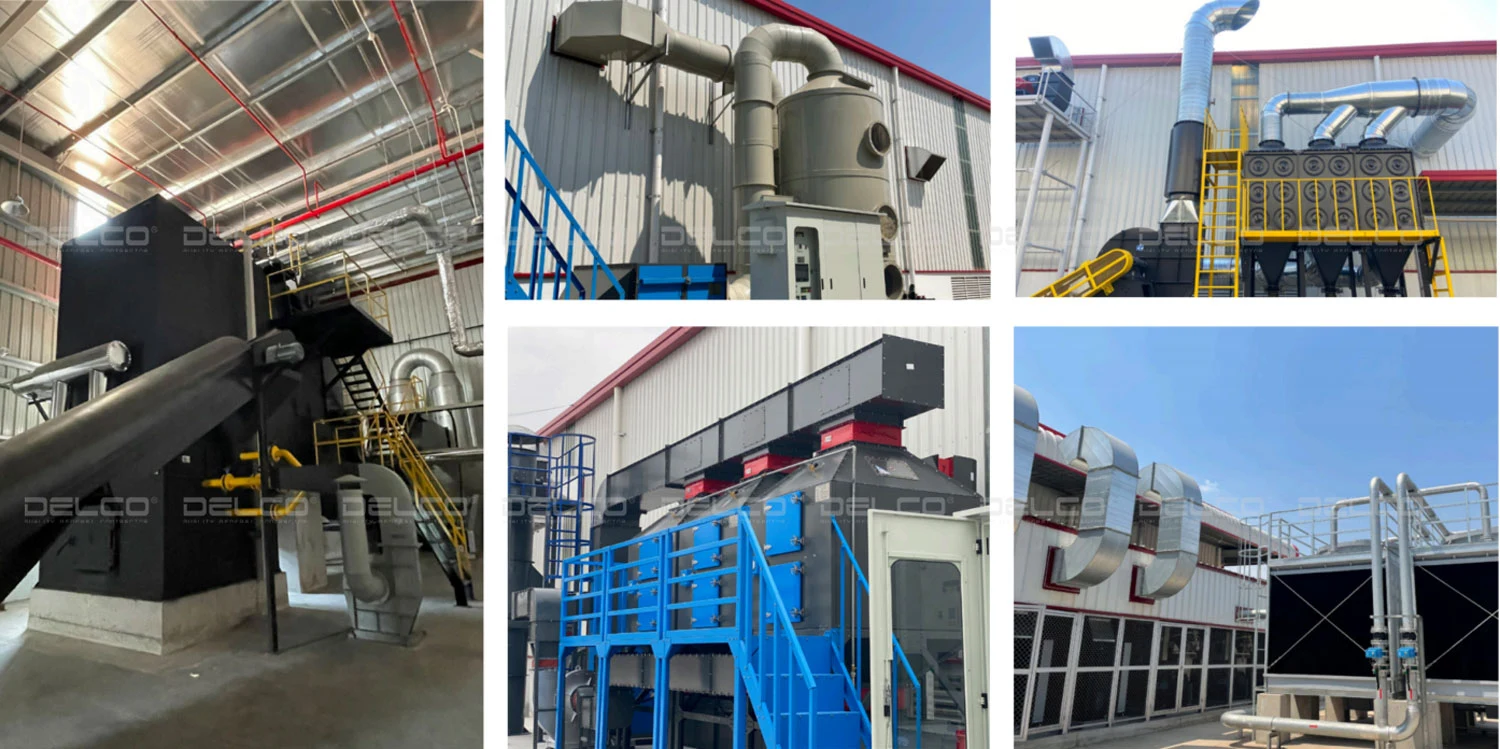
2. Selecting materials to ensure system safety and longevity
Electrical materials must have clear origins and technical certificates according to international standards. Key material groups include:
2.1. Electrical cables
- Certificates of Origin (CO) and Quality (CQ); comply with IEC 60228 (conductors) and IEC 60502-1/-2 (medium–low voltage cables).
- Fire-resistant zones require FR/LSZH cables per IEC 60332, IEC 60331.
- Cable size selection based on allowable current, voltage drop, ambient temperature, and installation method.
2.2. Busway
- Complies with IEC 61439-6, ensuring short-circuit withstand capability, IP/IK protection levels, and thermal stability.
- Ideal for large-scale factories requiring reliable and easily expandable power distribution.
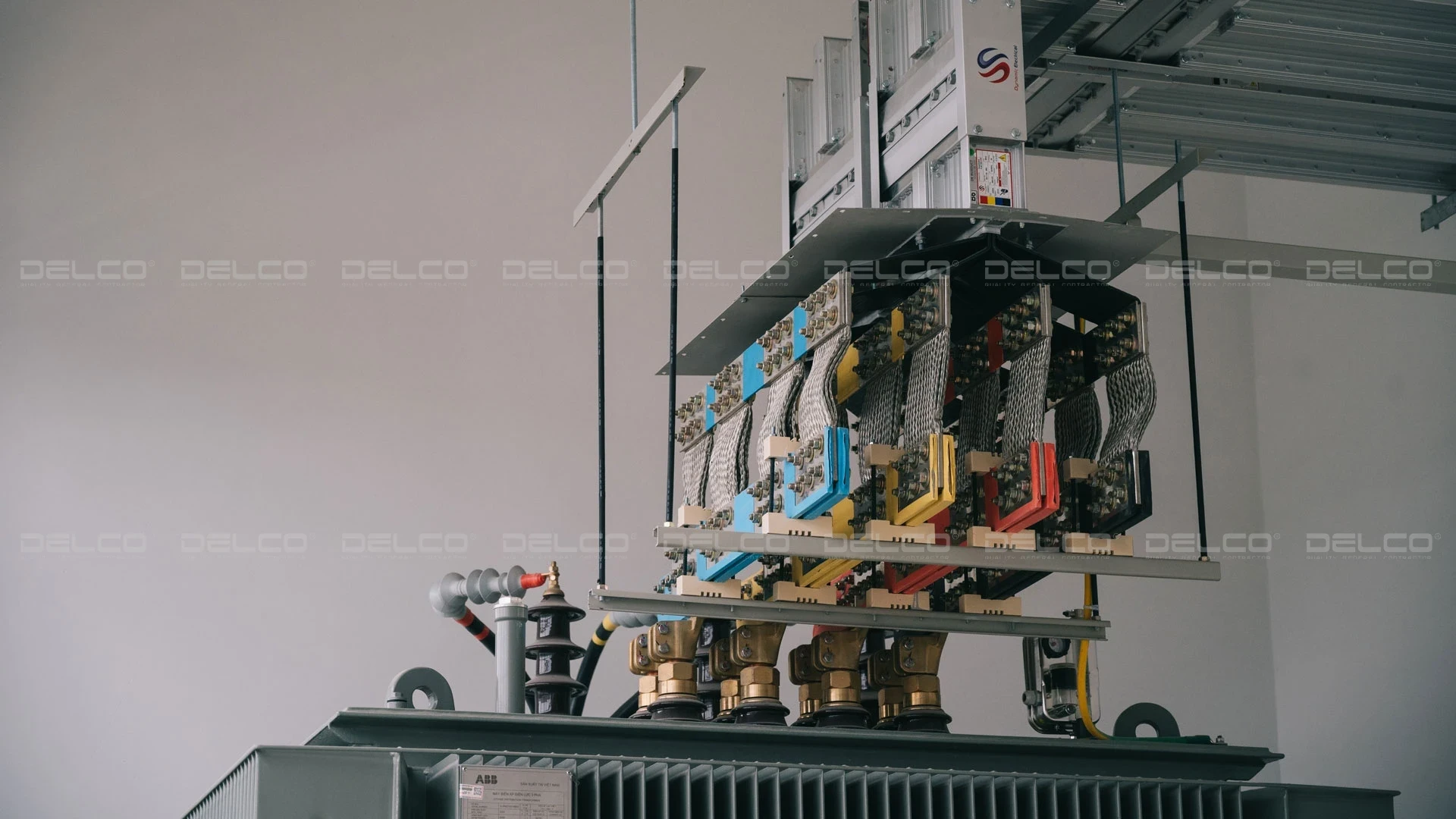

Busway system for DORCO Living Vina factory at Hoa Mac Industrial Park, Ha Nam
2.3. Electrical cabinets – MCCB – ACB
- Cabinets per IEC 61439-1/-2; circuit breakers per IEC 60947.
- Devices commonly selected from Schneider, ABB, LS… to ensure reliability and long-term replaceability.
- Focus on specifications: breaking capacity (Icu/Ics), selectivity, IP rating, and fire safety compliance.
2.4. Earthing and lightning protection devices
- Earthing: Materials (rods, cables) must provide good conductivity and corrosion resistance for soil conditions. Copper or copper-bonded steel rods typically require ≥99.9% Cu layer per standards/manufacturer. Underground joints should use exothermic welding per UL/ASTM for durability.
- Surge protection devices (SPD): Must be IEC 61643-certified and have appropriate Voltage Protection Level (Up).
2.5. Lighting fixtures and outlets
- Lighting: Requirements for luminous efficacy (Lumen/Watt), color rendering index (CRI), and lifespan L70/B50 (usually >50,000 hours).
- Sockets/Switches: Load-bearing capability, flame-retardant materials, and IP rating appropriate for the production environment.
2.6. Cable trays – ladder trays – accessories
- Cable trays: Powder-coated, corrosion-resistant; thickness and load capacity must follow JIS/ASTM. For outdoor or humid areas, hot-dip galvanized coating (HDG) thickness should be checked.
- Connection accessories: Lugs and busbars must have high conductivity, good heat resistance, and UL or CSA certification.
- Conduits: Require appropriate thickness, flame resistance, and galvanization (for steel conduits).
2.7. Material inspection before installation
- Cross-check catalogues, models, specifications.
- Inspect appearance, dimensions, coating, batch numbers.
- Verify CO/CQ, IP, IK ratings, and factory test reports.
DELCO has many years of experience as a general contractor for construction and M&E (mechanical and electrical) for large-scale FDI projects. With deep understanding of technical standards, operational requirements, and the specifics of each manufacturing sector, DELCO consistently delivers synchronized design solutions, selects standard-compliant materials, optimizes costs, and ensures long-term safety and stability for factory electrical systems. This foundation gives investors peace of mind when launching new projects or expanding capacity.