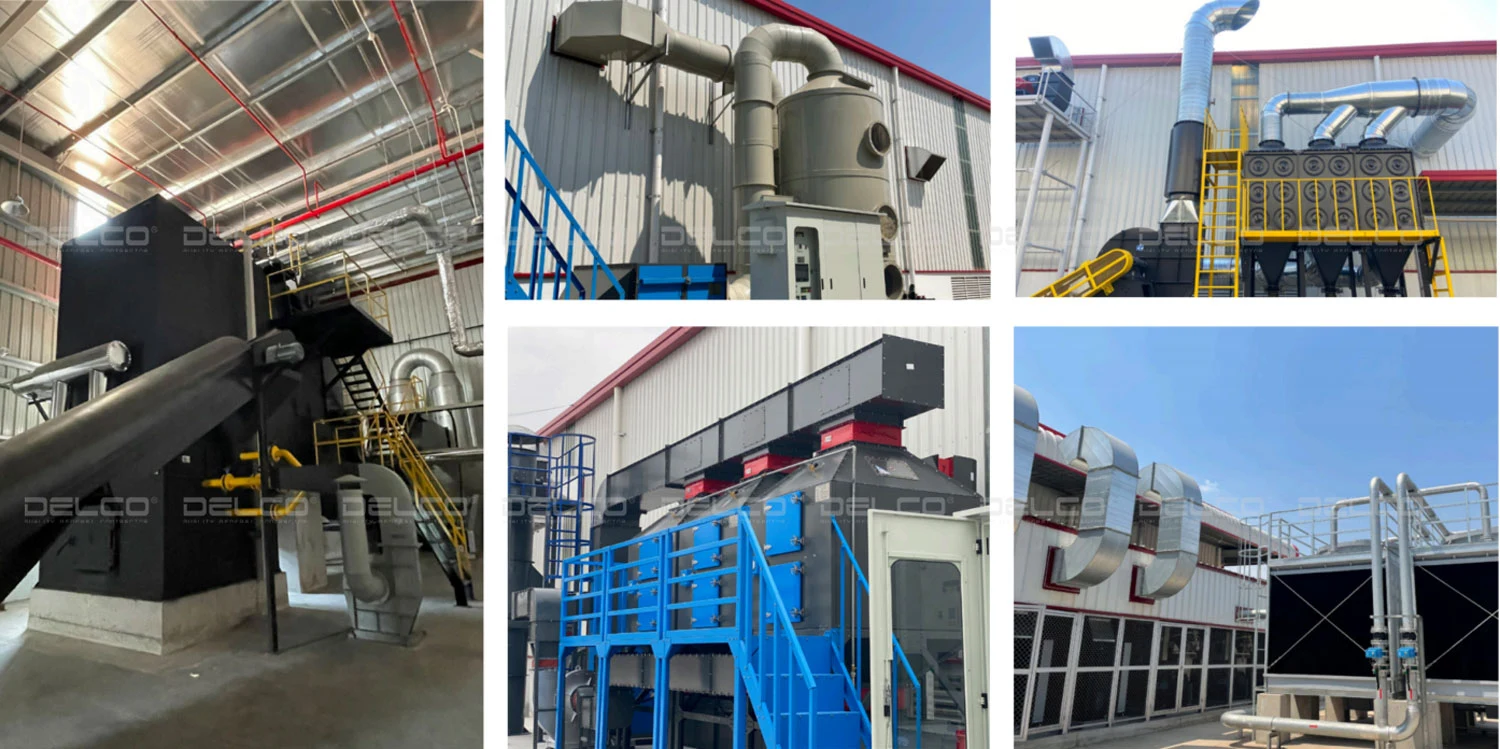
In the pharmaceutical and food industries, especially factories producing functional foods or export goods, GMP standards require strict control over the production environment, including cleanroom areas, to ensure high product quality, safety, and contamination prevention. The HVAC system plays a critical role in maintaining key parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and air quality, helping to prevent cross-contamination, microbial growth, microorganisms and dust, while ensuring compliance with standards such as ISO 14644 and HACCP
Specific HVAC requirements for GMP-compliant factories
For pharmaceutical factories
According to guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO) and EU-GMP, HVAC systems in pharmaceutical manufacturing must meet the following strict requirements:
- Controlled environment: Production must take place in a strictly controlled environment, where the HVAC design is closely coordinated with the facility layout to prevent external contamination and cross-contamination between production areas.
- Air filtration: HEPA filters (H13 or equivalent, as per EN 1822) must be used to maintain air cleanliness, especially in sensitive areas such as cleanrooms or raw material handling zones.
- Pressure differentials: Positive pressure (typically 10–15 Pa) must be maintained in cleanroom areas compared to adjacent zones, supported by pressure sensors and automatic alarms when thresholds are exceeded.
- Temperature and humidity control: Temperature and humidity must be continuously monitored and recorded to maintain conditions suitable for materials, products, and staff comfort. Minimum and maximum values must be clearly defined—commonly 18–26°C and 40–60% RH.
- Airflow and distribution: Ensure fast recovery time (less than 15 minutes) and even air distribution throughout the space. AHU (Air Handling Unit) downtime should be avoided unless there is a justified reason.
- Monitoring and alarms: The system should use SCADA or IoT platforms with integrated sensors to measure airflow, pressure, and temperature, and trigger alarms when parameters exceed set limits.
- Maintenance and validation: HEPA filters, valves, ducts, and fans must be regularly maintained. Leak testing is required after each filter replacement. The system must be validated according to ISO 14644, based on a documented risk assessment.
For food factories
In food factories, HVAC requirements may vary depending on the type of food and production process, but they generally focus on the following key aspects:
- Temperature and humidity control: To prevent microbial growth and ensure proper storage conditions for raw materials and finished products. A common target is 20–25°C and relative humidity below 60%, especially for functional foods or products intended for export.
- Air quality: Use of efficient air filters to remove dust, bacteria, and airborne contaminants, ensuring a hygienic production environment.
- Compliance with HACCP and GMP: For export-oriented factories, compliance with international standards like HACCP is mandatory. The HVAC system must support the required hygiene conditions, especially in production, packaging, and storage areas.
- Monitoring and alarms: Manual or simple automated monitoring systems can be used (depending on the type of food), with logging of temperature and humidity and alarms when thresholds are exceeded.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and cleaning of filters, valves, air ducts, and fans, with a focus on hygiene and operational efficiency.


HVAC system implemented by Delco
Comparison of HVAC requirements between pharmaceutical and food factories
| Factor | Pharmaceutical factory | Food factory |
| Applicable standards | GMP (WHO, EU, FDA), ISO 14644 | GMP, HACCP, local standards (e.g., QCVN 01-1:2018/BYT in Vietnam) |
| Air filtration | HEPA filters (H13 or equivalent) for cleanrooms | High-efficiency filters; HEPA not always required, depending on food type |
| Pressure differential | Mandatory; positive pressure in clean areas | Optional, but recommended in sensitive zones such as packaging |
| Temperature/humidity control | Strict control with defined minimum and maximum limits | Controlled to prevent microbial growth; generally less strict than pharmaceuticals |
| Monitoring | Automated system integrated with GxP; alarms triggered when limits are exceeded | Regular monitoring; complex automation not always necessary |
| Maintenance | Strict preventive maintenance program with detailed records | Routine maintenance focused on hygiene and operational efficiency |
Selecting an HVAC contractor for factory fit-out projects
Choosing the right HVAC contractor is a key factor in ensuring that the system meets GMP standards, operates efficiently, and minimizes long-term costs. Below are important criteria to consider:
- Experience and expertise: Select contractors with proven experience in pharmaceutical or food projects. They should have a deep understanding of WHO, EU GMP, HACCP, and ISO 14644 standards, and be capable of precisely controlling temperature, humidity, pressure, and air quality.
- Turnkey solutions: Give priority to contractors who offer end-to-end services — from design, installation, validation to maintenance — ensuring the system suits the specific needs of the project and reduces coordination risks.
- Modern technology: Contractors should integrate IoT, SCADA systems, or real-time sensors to monitor environmental conditions, enable predictive maintenance, and optimize energy use (potentially reducing operating costs by 15–20%).
- Financial transparency: Require a clear and detailed quotation, including installation costs (typically 10–20% of the total fit-out budget) and long-term maintenance. Contractors should also provide company profiles and international certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Construction timeline: Ensure a clear schedule (usually 3-6 months for complex HVAC systems), with a firm commitment to on-time delivery and post-installation support.
- Long-term support: Contractors should provide a preventive maintenance plan, including regular inspection of filters, valves, ducts, and fans, along with fast-response repair services.
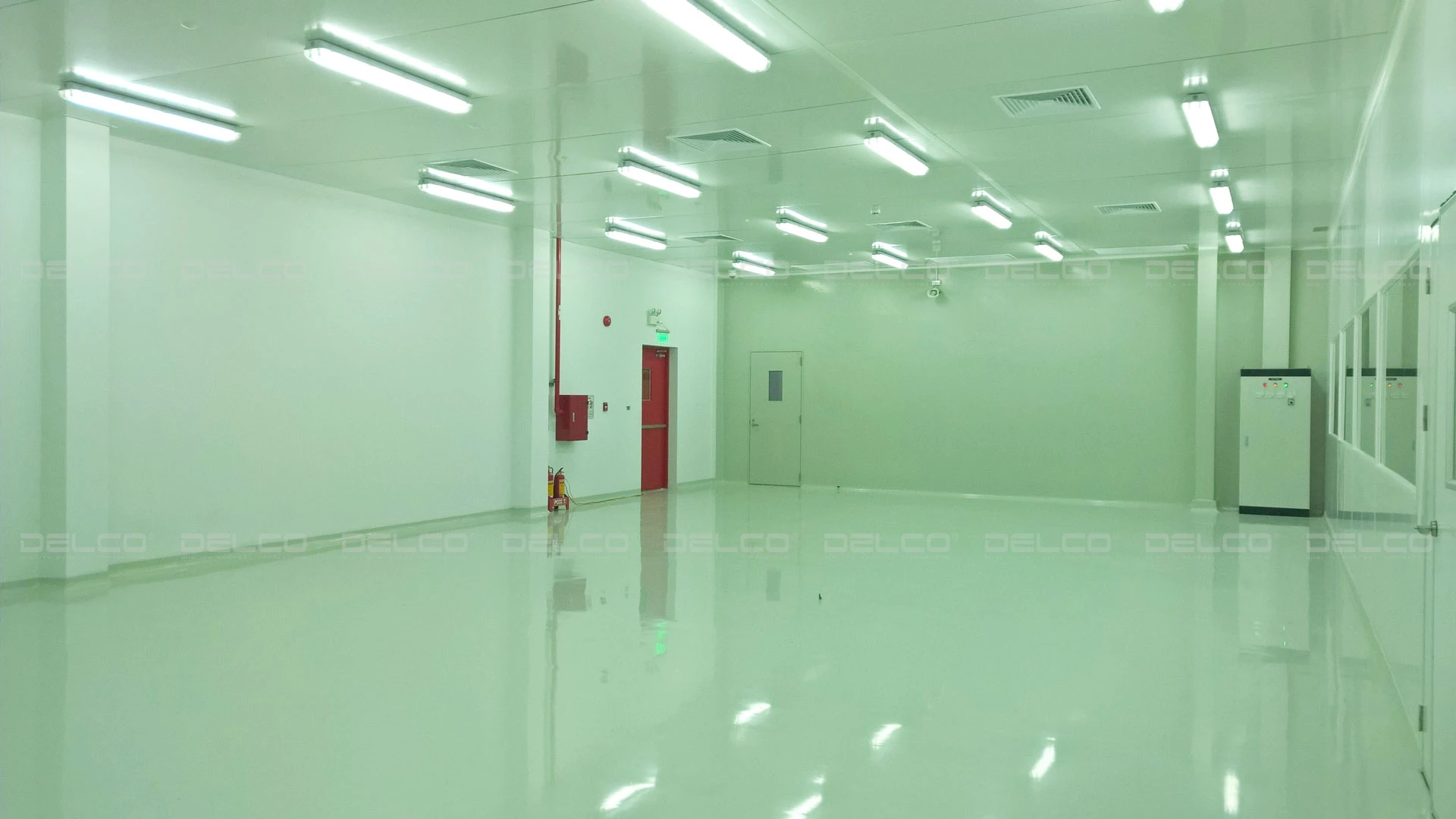

Cleanroom at Pham Nguyen food and confectionery processing factory, Hung Yen
By meeting strict technical requirements and selecting a reputable contractor, investors can build a factory that runs efficiently, complies with international standards, and delivers long-term cost savings.
See more: Integrated factory fit-out process from design to construction in Vietnam
See more: Key changes in factory fitout in 2025
See more: HVAC technology trends in Vietnam in 2025