The lighting system in industrial factories not only optimizes work efficiency but also plays a crucial role in shaping the factory space, enhancing aesthetics, and ensuring harmony with the overall architectural design.
Lighting systems in factory architecture
Ambient lighting
Ambient lighting serves as the primary light source, ensuring uniform brightness and setting the overall tone for the entire factory space. Common types of ambient lighting include LED panels, LED highbay lights, and LED tubes, which are typically installed on the ceiling to provide wide light coverage, minimize shadows, and ensure clear visibility.
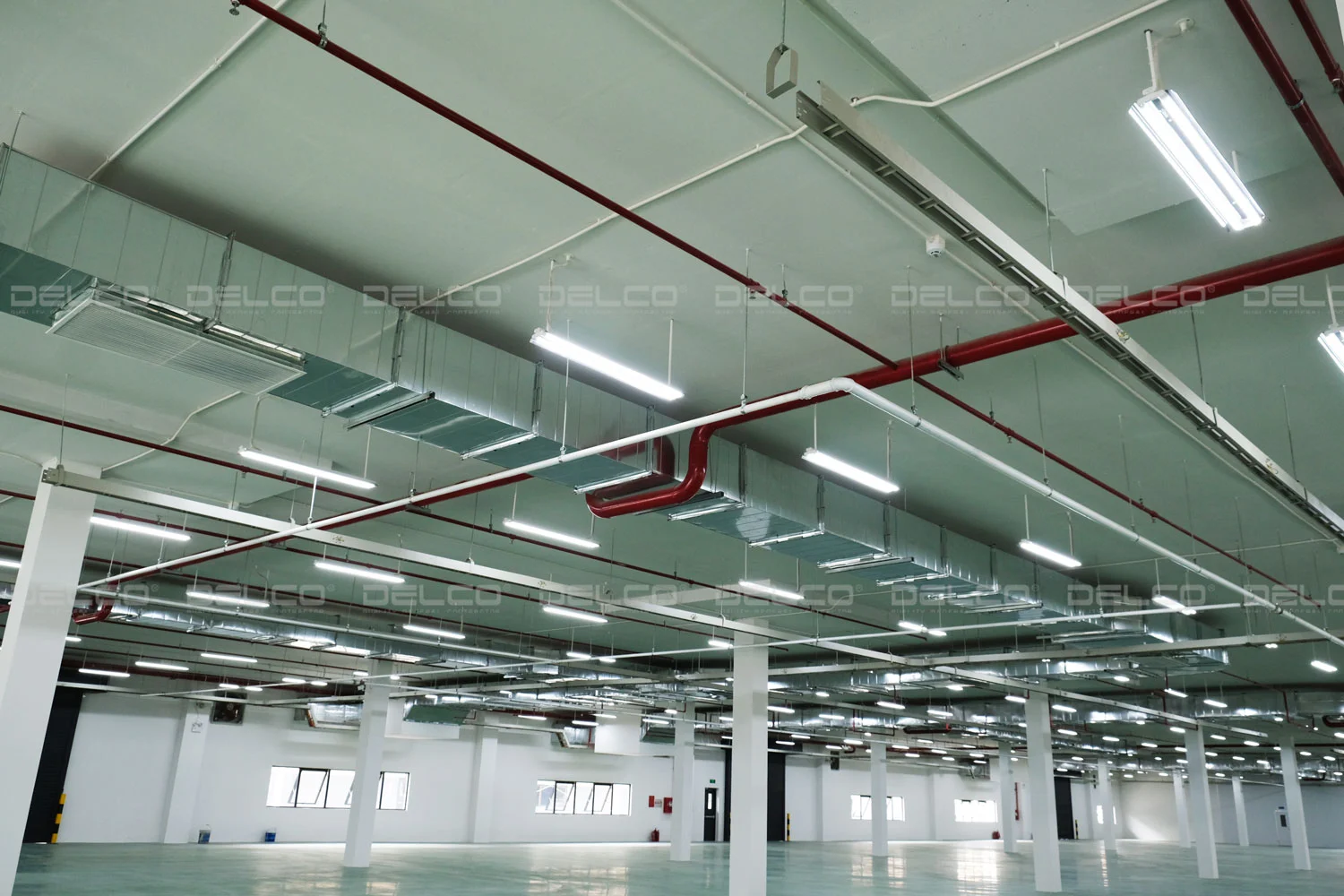

Task lighting
In addition to general lighting, certain areas in factories require task lighting to support work that demands high precision. Task lighting is commonly used in areas such as production lines and product inspection zones, especially in industries like electronic component assembly and mechanical processing. Desk lamps, directional LED lights, and machine-mounted lights are popular choices that help reduce eye strain, improve accuracy, and minimize errors.
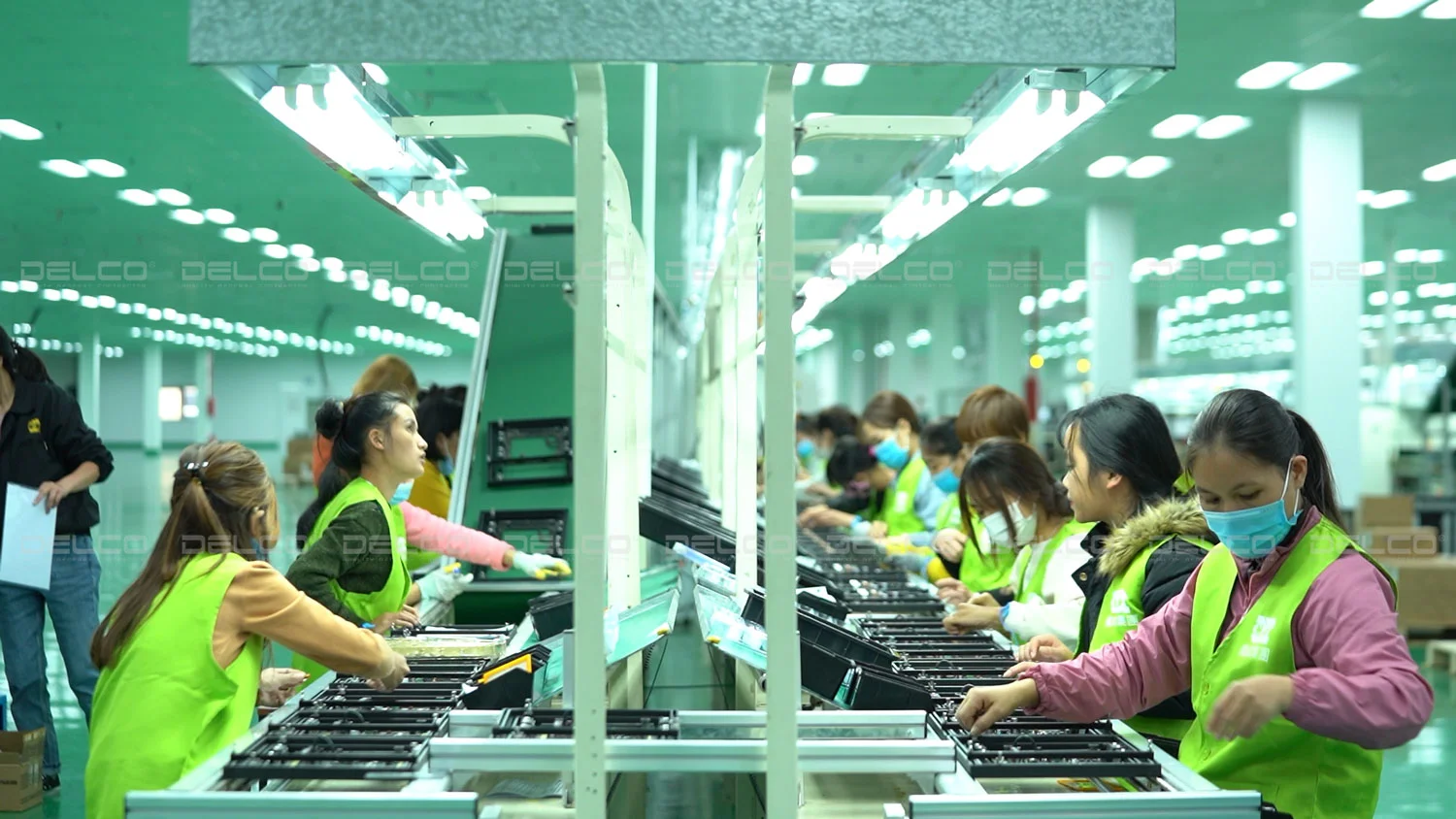

Accent lighting
Beyond production-focused lighting, accent lighting is used to highlight key architectural elements within the factory, such as reception areas, company logos, signage, or walkways. The main purpose of this system is to enhance aesthetics, reinforce brand identity, and aid in spatial orientation. Common accent lighting options include spotlights, wall washers, and LED downlights, which create special lighting effects and emphasize architectural features.
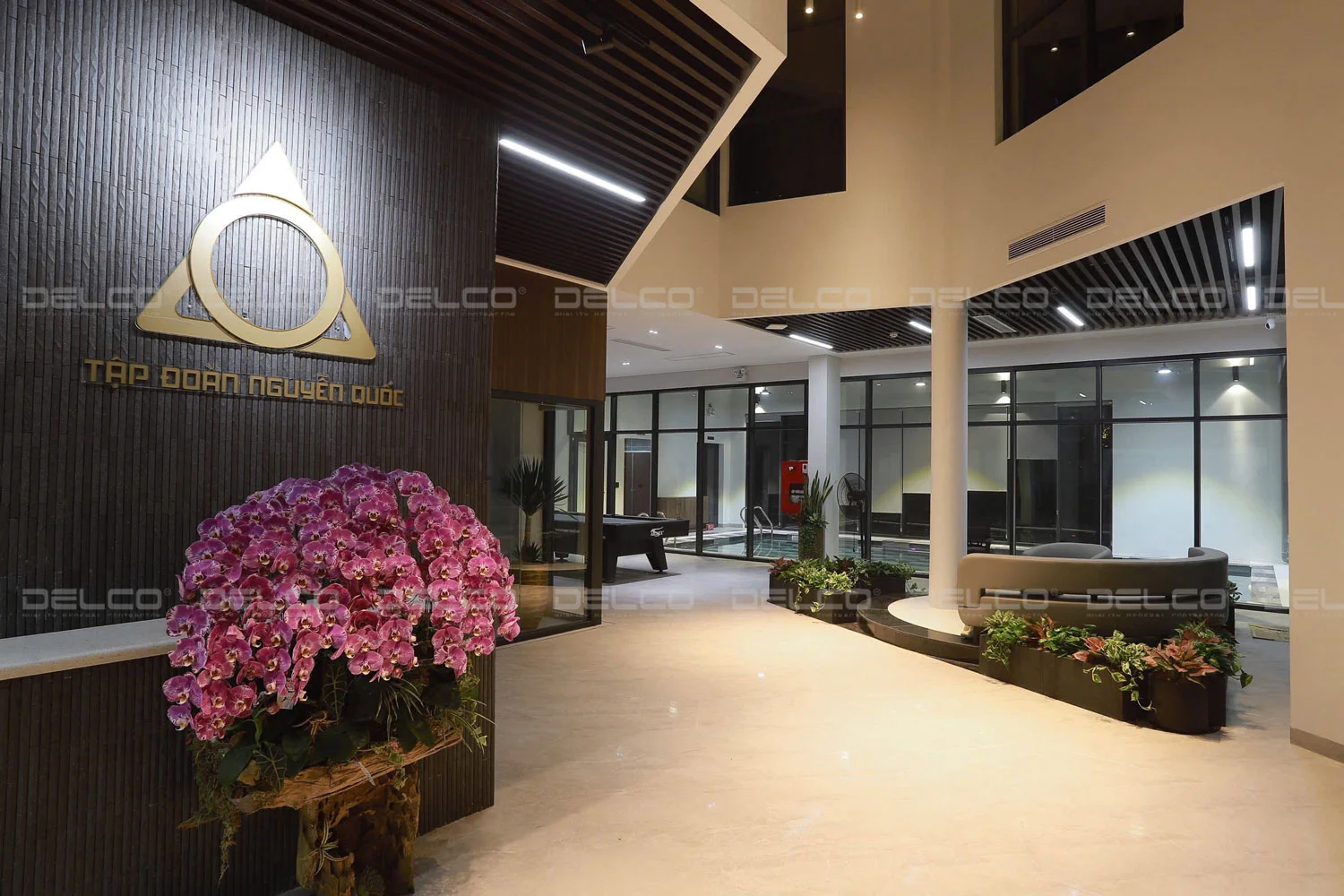

Optimal lighting design solutions for factories
Choosing the right color temperature for each space
Color temperature plays a crucial role in creating a productive and comfortable working environment. In offices, meeting rooms, and production areas, cool lighting (4000K – 6500K) helps maintain alertness and focus. On the other hand, warm lighting (2700K – 3500K) is more suitable for relaxation areas such as cafeterias, reading corners, and reception areas, providing a cozy and comfortable atmosphere.

In factory and warehouse lighting design, cool lighting is commonly used to enhance workers’ concentration.

Meanwhile, warm lighting is often preferred in office areas such as reception zones and cafeterias to create a welcoming and professional environment.
Balancing natural and artificial lighting
Integrating natural and artificial lighting in factories not only reduces energy consumption but also strengthens the connection with the outside environment, positively impacting workers’ health, improving focus, and boosting productivity.
When designing a lighting system, MEP contractors should consider incorporating large windows, skylights, or transparent materials such as tempered glass and light-transmitting metal sheets to maximize natural light intake. Additionally, artificial lighting should be strategically arranged to compensate for dim areas, preventing excessive contrast between different sections and ensuring uniform illumination throughout the factory.

Lighting design aligned with wall colors and interior materials
Wall colors and interior materials significantly impact lighting efficiency. Light-colored walls, such as white or light gray, reflect light better, reducing the number of fixtures needed. In contrast, dark-colored ceilings and walls or materials that absorb light require higher-powered lighting systems or additional task lighting to ensure adequate brightness in the workspace.
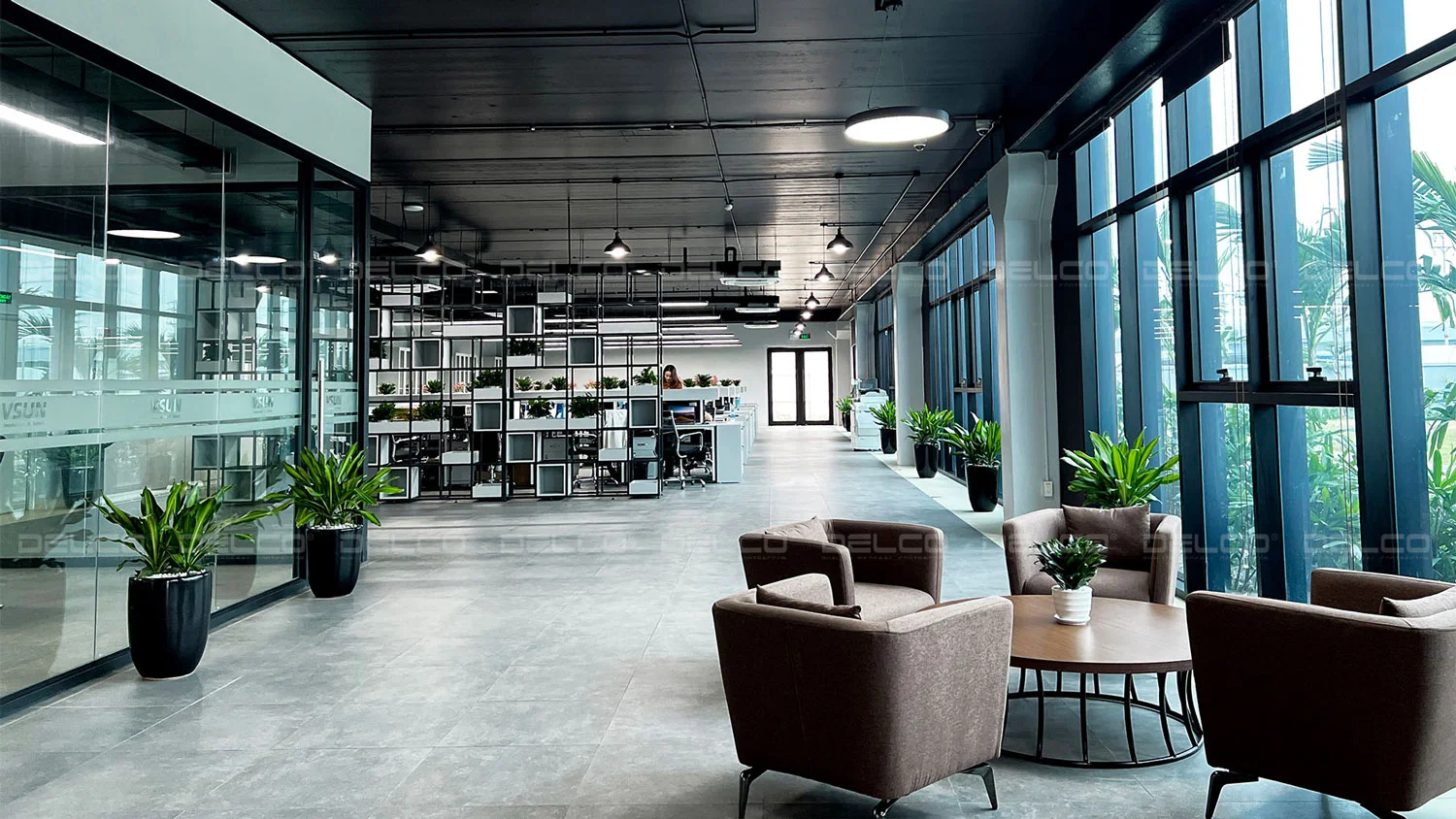

Lighting design for aesthetics and architectural consistency
The design of lighting fixtures should align with the overall architectural style to create harmony, enhance aesthetics, and maintain consistency throughout the factory.
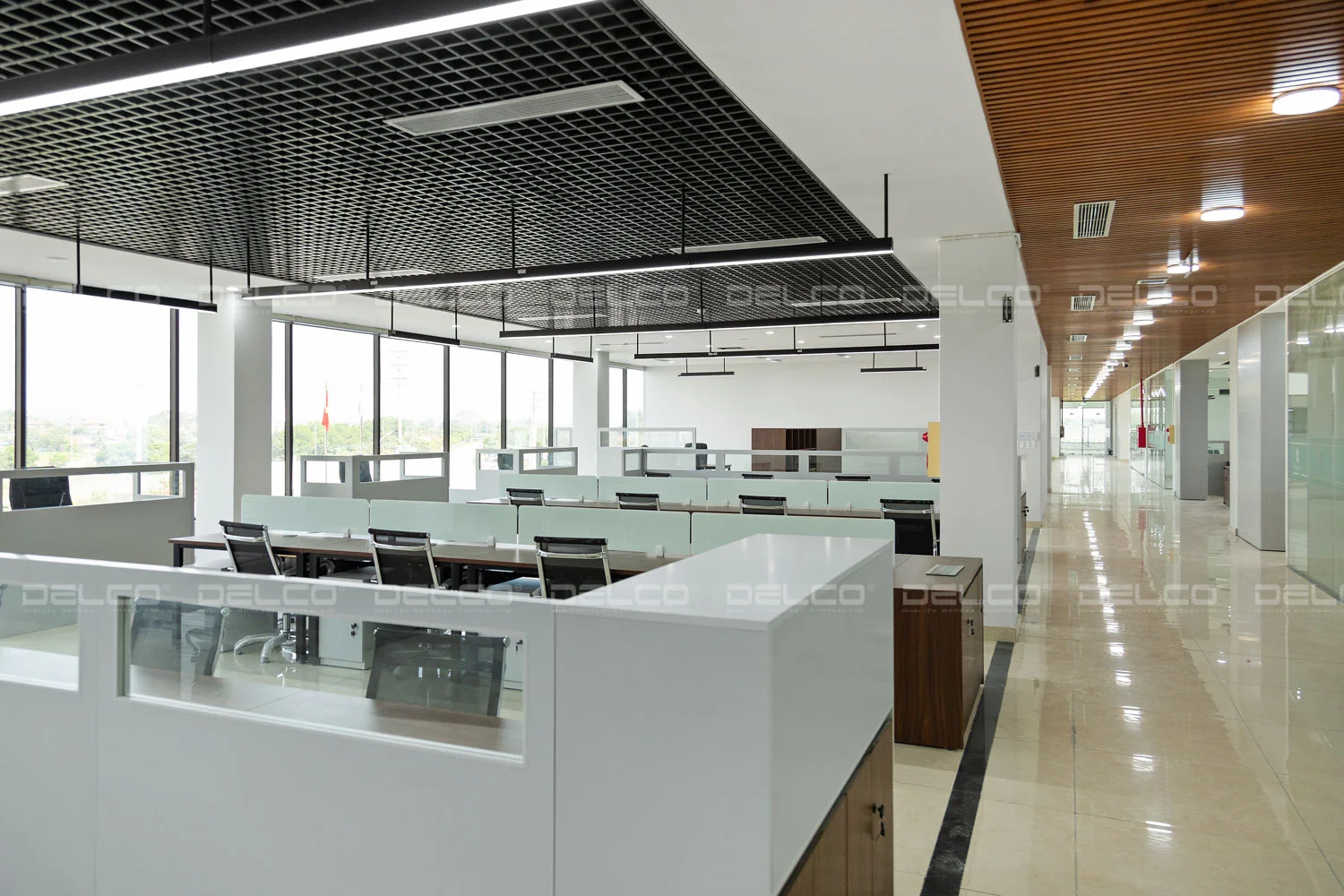

In high-end factory offices, linear or panel LED lights are popular choices, offering a clean, modern, and minimalist look. For walkways or outdoor landscapes, accent lighting can be used to enhance aesthetics and highlight key areas.
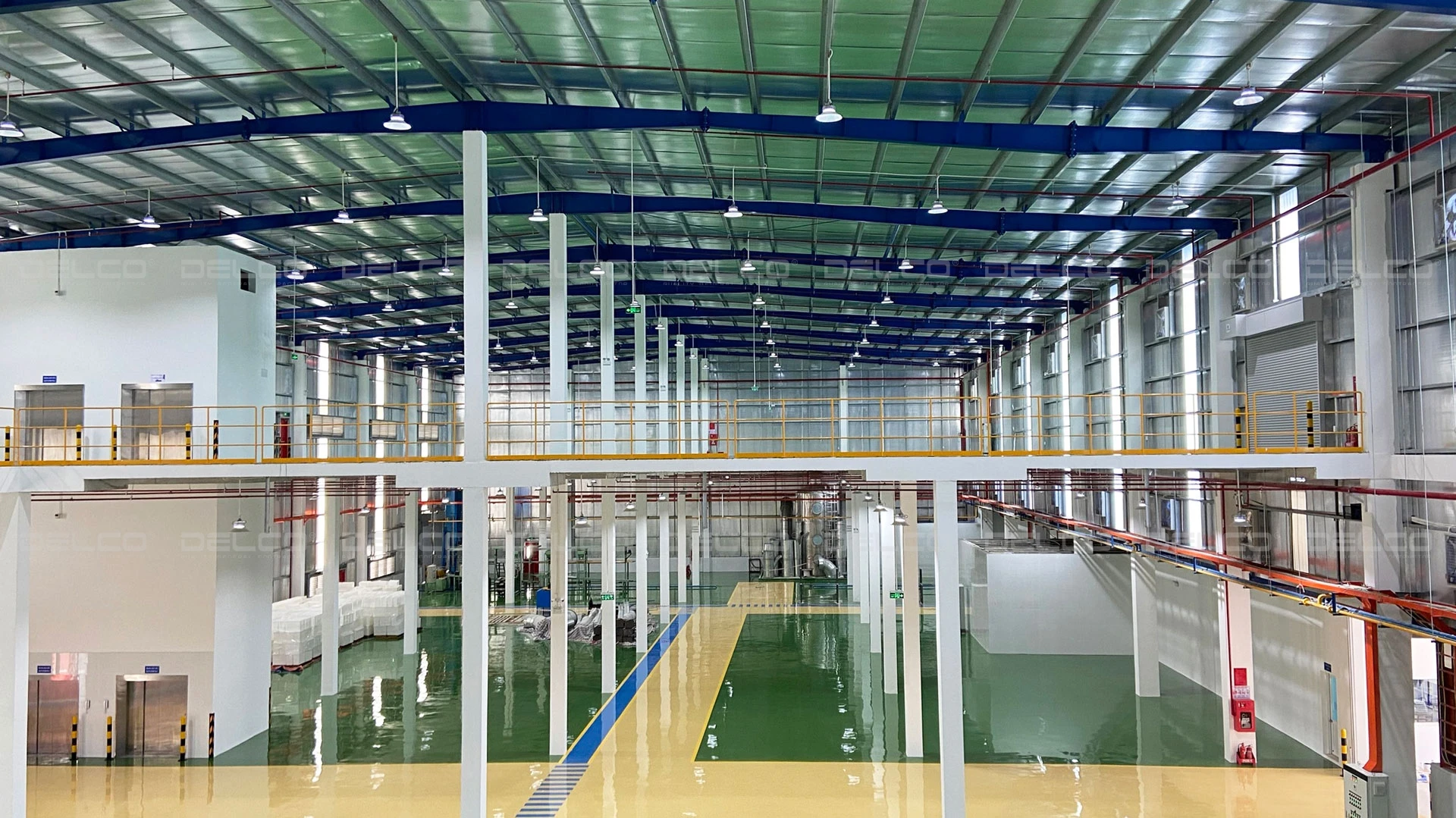

For large production areas with high ceilings and steel-frame structures, UFO or dome-shaped LED highbay lights are commonly used due to their high power, wide beam angle, and durable design, ensuring strong performance in industrial environments.
See more : Vietnamese lighting standards for workshops and factories
See more : Common mistakes in factory lighting design