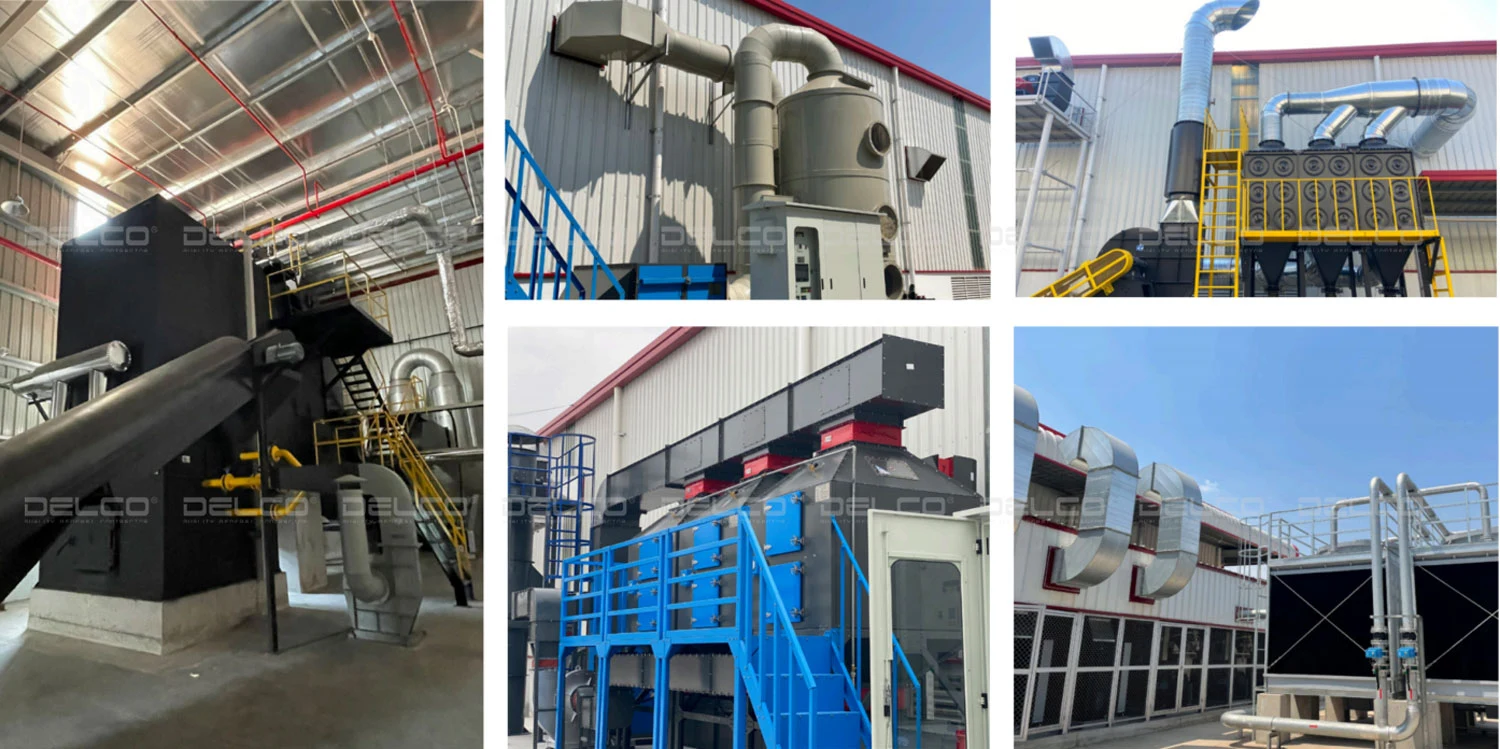
For industrial plants that generate wastewater during production processes, a wastewater treatment system is a mandatory requirement for obtaining operational and production permits.
What is an industrial wastewater treatment system?
An industrial wastewater treatment system is a collection of equipment and technologies used to remove pollutants from wastewater generated by factories. Industrial wastewater often contains heavy metals, chemicals, and microorganisms that can pollute the environment if left untreated. This system ensures that wastewater meets environmental standards before being discharged outside, following specific regulations. The wastewater treatment system is typically part of the plumbing component within the MEP system to ensure consistency throughout the facility.

Depending on production needs and characteristics, businesses can choose different wastewater treatment methods such as physical, chemical, or biological processes. Factory wastewater must meet the standards specified in Column A or Column B of QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT before being discharged into the environment.
| Index Number | Parameter | Unit | Value C | |
| A | B | |||
| 1 | Temperature | °C | 40 | 40 |
| 2 | Color | Pt/Co | 50 | 150 |
| 3 | pH | – | 6 to 9 | 5,5 to 9 |
| 4 | BOD5 (20oC) | mg/l | 30 | 50 |
| 5 | COD | mg/l | 75 | 150 |
| 6 | Suspended Solids | mg/l | 50 | 100 |
| 7 | Asen | mg/l | 0,05 | 0,01 |
| 8 | Mercury | mg/l | 0,005 | 0,01 |
| 9 | Lead | mg/l | 0,1 | 0,5 |
| 10 | Cadimi | mg/l | 0,05 | 0,1 |
| 11 | Crom (VI) | mg/l | 0,05 | 0,1 |
| 12 | Crom (III) | mg/l | 0,2 | 1 |
| 13 | Copper | mg/l | 2 | 2 |
| 14 | Zinc | mg/l | 3 | 3 |
| 15 | Niken | mg/l | 0,2 | 0,5 |
| 16 | Mangan | mg/l | 0,5 | 1 |
| 17 | Iron | mg/l | 1 | 5 |
| 18 | Total Cyanide | mg/l | 0,07 | 0,1 |
| 19 | Total Phenol | mg/l | 0,1 | 0,5 |
| 20 | Total Mineral Oil and Grease | mg/l | 5 | 10 |
| 21 | Sunfua | mg/l | 0,2 | 0,5 |
| 22 | Flo | mg/l | 5 | 10 |
| 23 | Ammonium (calculated as N) | mg/l | 5 | 10 |
| 24 | Total Nitrogen | mg/l | 20 | 40 |
What does a wastewater treatment system consist of? – Basic structure of a wastewater treatment system
A factory’s wastewater treatment system typically includes essential components such as an oil and grease separator, trash screen, sand settling tank, equalization tank, aeration tank, and disinfection tank. Each component in the wastewater treatment system has a specific role, helping to remove impurities and pollutants from the wastewater before it is discharged into the environment.
- Oil and Grease Separator / Septic Tank: Used to treat wastewater from areas like cafeterias and kitchens. It functions to separate animal and vegetable oils and greases or certain oils used in production from the wastewater.
- Trash Screen: Removes suspended solids and larger debris from the wastewater.
- Sand Settling Tank: Captures suspended inorganic particles that are small, hard, and denser than water, allowing them to settle quickly.
- Equalization Tank (Collection Tank): Regulates the stability of wastewater quality, flow rate, and pH level.
- Primary Sedimentation Tank: Separates suspended particles, allowing solid particles to settle at the bottom.
- Anoxic Tank: Treats nitrogen and phosphorus present in the wastewater.
- Aeration Tank – Aerotank: Dissolves and decomposes organic substances, converting them into biomass consisting of water and CO₂. Microorganisms gather as activated sludge flocs.
- Secondary Sedimentation Tank: After being filtered in the aeration tank, wastewater flows to this tank, where biological sludge settles, and the remaining water flows into the disinfection tank.
- Disinfection Tank: Wastewater is treated with disinfection methods, often using chemicals with strong sterilization effects (e.g., chlorine, CaOCl₂) before being discharged into the environment.
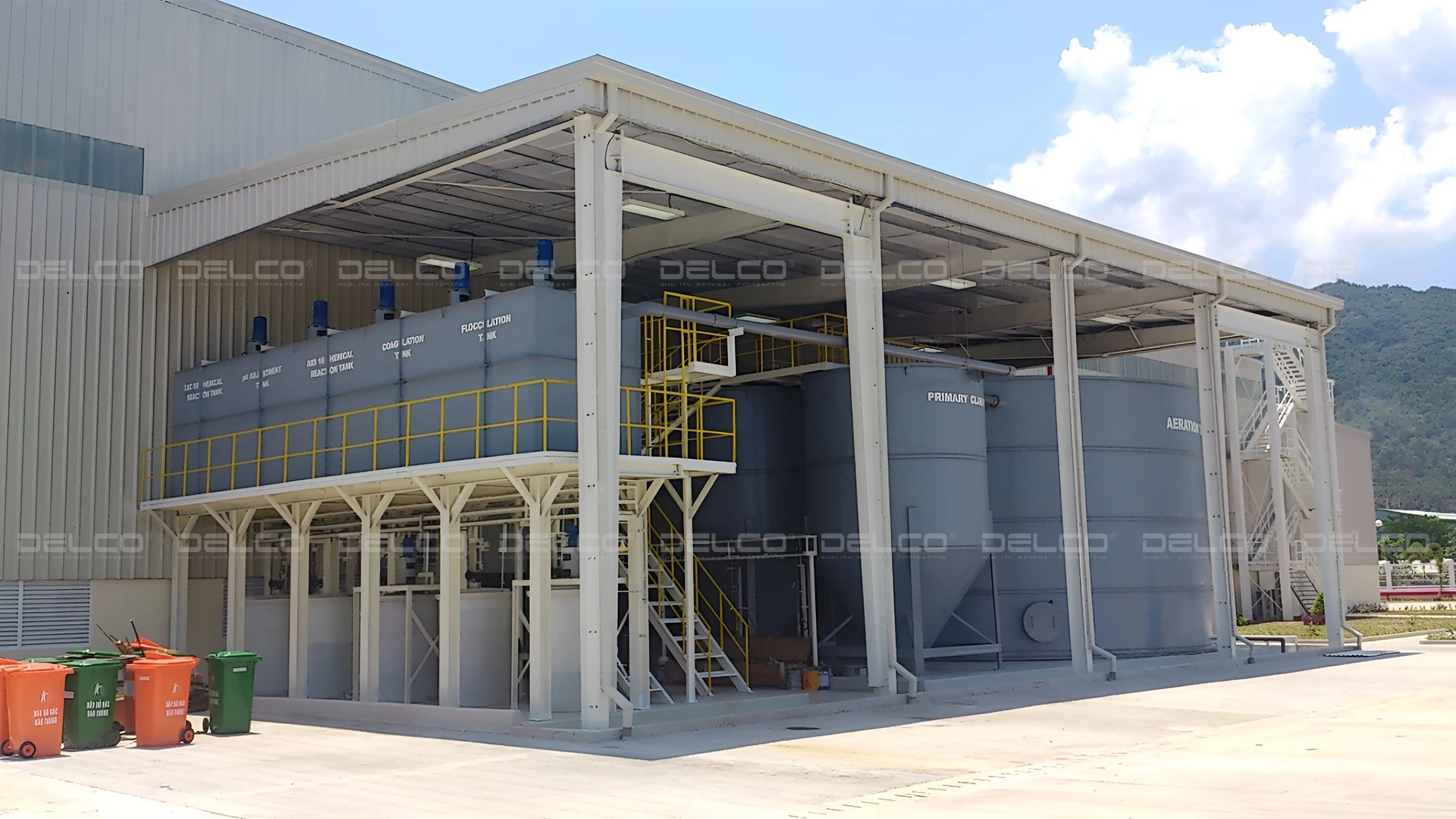

Depending on the characteristics of the wastewater and regulatory discharge requirements that the factory must follow, each company can adjust the design and structure of their factory’s wastewater treatment systems.
Role of the wastewater treatment system in factories
A wastewater treatment system (WWTS) is a crucial component for factories aiming to operate sustainably and comply with environmental protection regulations, meeting strict green production standards required by international organizations and partners.
- Environmental Protection: Reduces pollution of water, soil, and air; prevents negative impacts on ecosystems, such as the destruction of aquatic life.
- Legal Compliance: Ensures that the factory adheres to environmental laws, meets the necessary conditions for production, and avoids penalties for violating environmental protection regulations.
- Resource Reuse: Some advanced wastewater treatment systems allow businesses to reuse water after treatment, reducing the consumption of clean water and saving on costs.
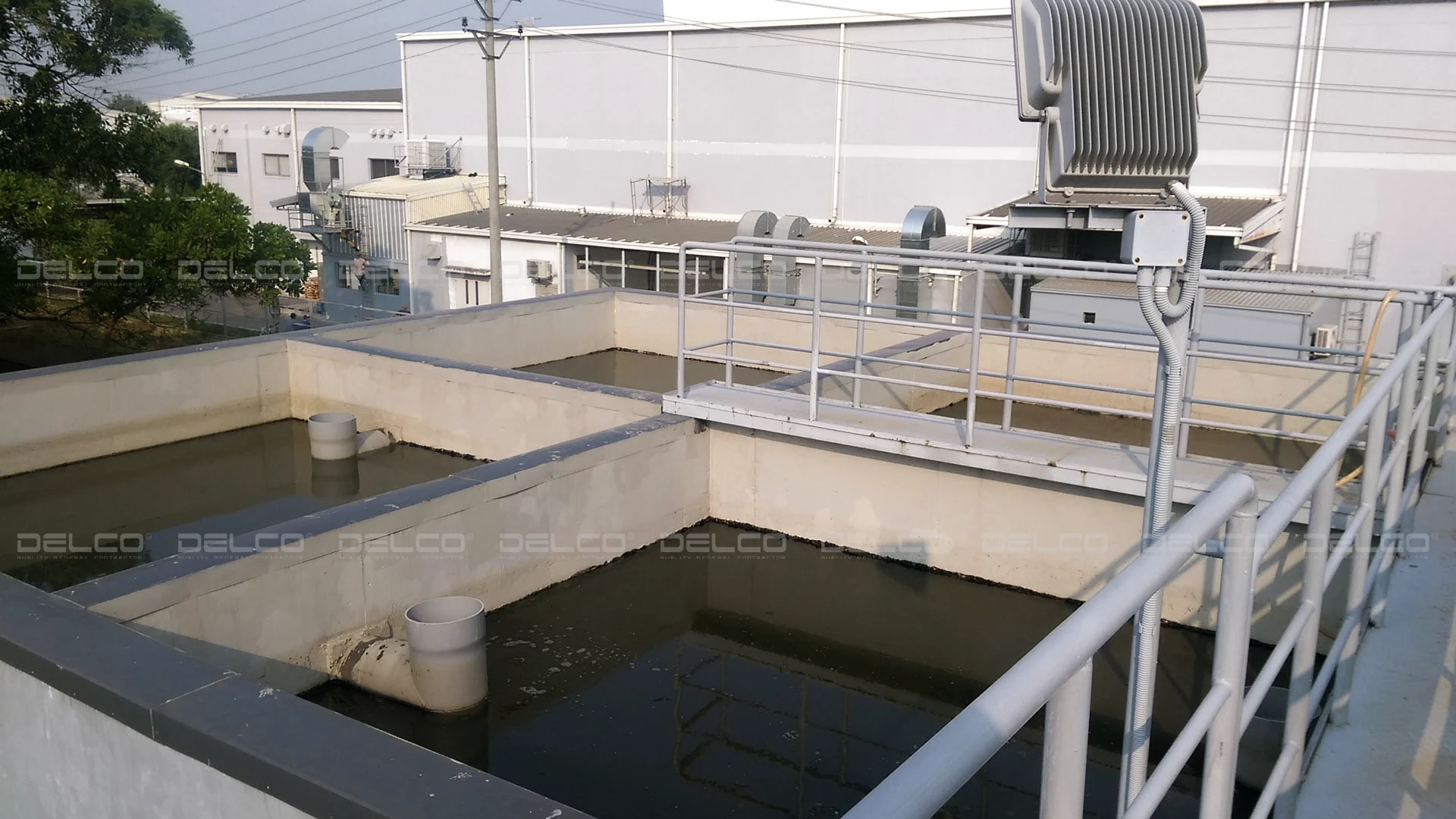

To comply with legal requirements and ensure efficient production, businesses need to regularly maintain their WWTS to keep it running smoothly, reduce the risk of breakdowns, and extend equipment lifespan. Additionally, factories with smaller volumes of wastewater may consider outsourcing industrial wastewater collection and treatment to third-party services to optimize costs.
See more: Typical Wastewater and exhaust gas treatment projects implemented by Delco
See more: Contact us to consult on the design of the factory’s mechanical and electrical systems