Factory design includes several crucial components such as master plan, architectural, and electrical systems design, etc. These components must be tightly integrated and synchronized to avoid conflicts, ensuring that the factory can put into operations safely and efficiently.
Rational master planning
For each factory, depending on the industry, production process, requirements for technology lines, and raw materials, there are various ways to function zoning and arrange the factory layout. However, there are certain principles that must always be adhered to ensure rationality and efficiency in the overall factory masterplan, such as:
- Carefully locate the positions of production areas related to each other, for example the raw material warehouses, and finished goods warehouses, to optimize traffic flow and minimize transportation costs within the factory;
- Production areas generating smoke, dust, and odors should be isolated and located at the end of the wind direction to avoid affecting other production areas;
- Locate separately production areas with different characteristics such as wet and dry production, clean rooms and dusty areas, high-noise production areas and office areas…
Additionally, compliance with QCVN 01:2021/BXD is an important factor when designing a factory that investors need to pay attention to. Investors must ensure that the maximum net construction density is 70%; For factory construction land lots with more than 5 floors used for production, the maximum net construction density is 60%. Furthermore, the green ratio of the factory also needs to reach a minimum of 20%.

Considering Operational and Maintenance Factors in Architectural Design
Architecture is a critical element in the design and construction of a factory. While meeting aesthetic requirements is important, investors must also pay close attention to the bearing capacity as well as the operational and maintenance processes of the factory. For example, skylights or stylized cover design options may be impressive and attractive on drawings, but in reality they can cause heat/sunlight in the factory or seepage or leak during rain due to insufficient sealing and less cover capabilities compared to traditional roofing structures.
Moreover, to enhance the longevity of the factory, investors should use durable materials that are suitable for local weather conditions, such as elastic paint and stainless steel. Additionally, Investors can consider choosing green materials and sustainable materials that can be reused to optimize costs, in accordance with current construction trends.

Checking and Early Handling Conflicts Between Architecture, Structure, and MEP
Combining systems involves creating integrated and synchronized drawings of the architectural, structural, and MEP systems of the factory on a single factory plan. This approach ensures precise positioning and elevation for each system, ensuring that all systems operate harmoniously and optimize the space for installation, operation, and maintenance of the factory efficiently. It adheres to technical requirements without compromising the aesthetics and functionality of the factory. Failure to integrate these systems can lead to situations where pipes, electrical lines, and mechanical equipment overlap, obstructing structural elements such as columns, beams, and load-bearing walls. This not only affects the construction timeline but can also lead to additional costs due to necessary adjustments or re-construction.
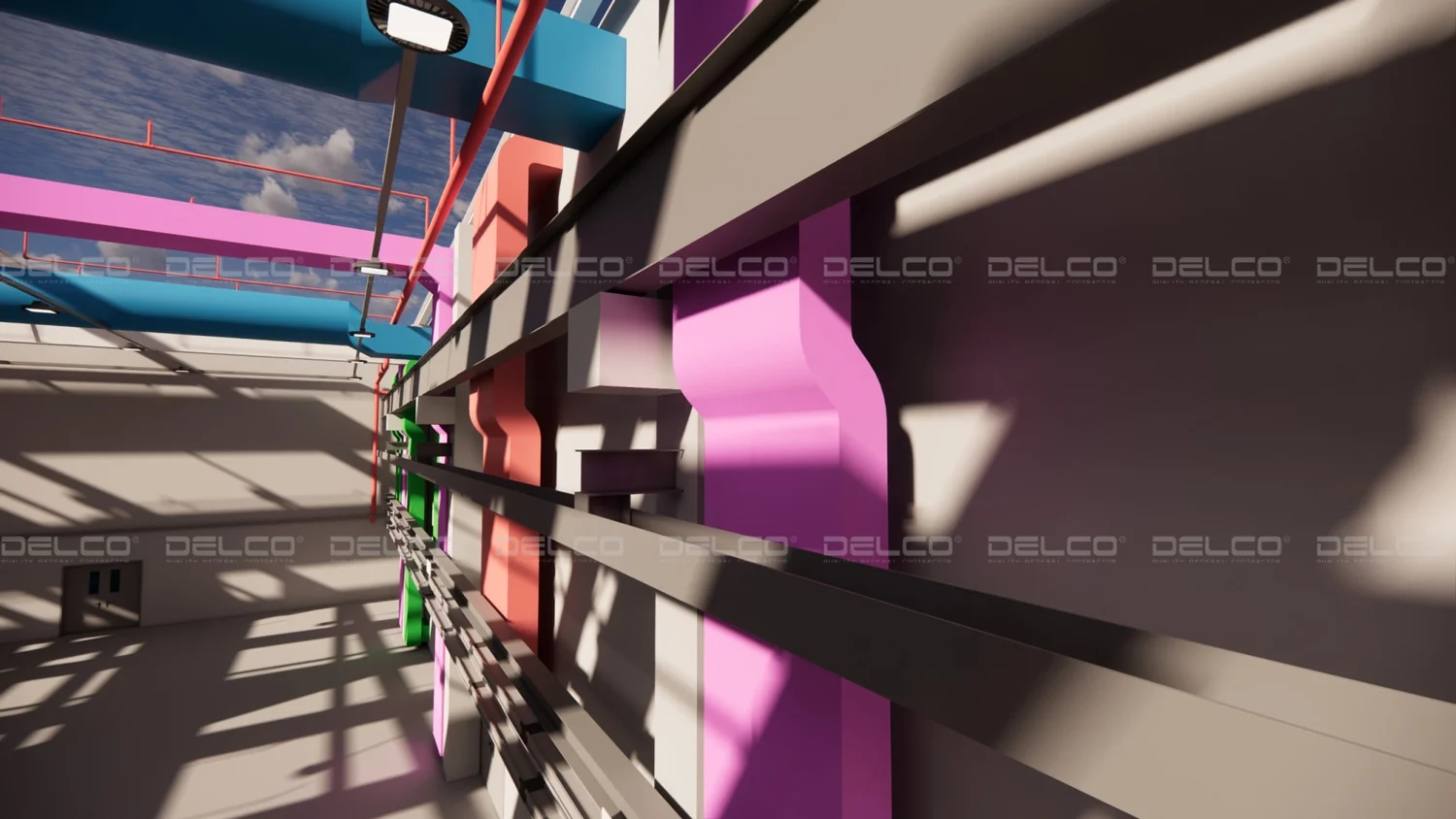

During the process of combining and handling conflicts between architecture, structure, and MEP, the load-bearing capacity is the top priority. When designing MEP systems, the design team needs to adjust the positions of conduits, electrical wiring, HVAC equipment, and more to avoid conflicts with beams and columns. In some cases where pipes must pass through floor beams and load-bearing structures, the design team must carefully calculate the load capacity and reinforcement methods to ensure technical requirements and feasibility during construction.
Calculating correctly and adequately the loads when designing the electrical system
The design team needs to have detailed discussions with the investor about the factory’s operational capacity and production lines to adequately calculate the load requirements. This ensures that the electrical system is designed to match the functionality of each area within the factory, promoting stable and efficient operation, and avoiding overloads that could damage equipment.
Additionally, the design team should also consider the factory’s future expansion plans, ensuring that the electrical system can be easily upgraded and expanded in future phases. This ensures that the electrical system will meet the operational needs of new production areas, helping the investor save time and costs effectively.
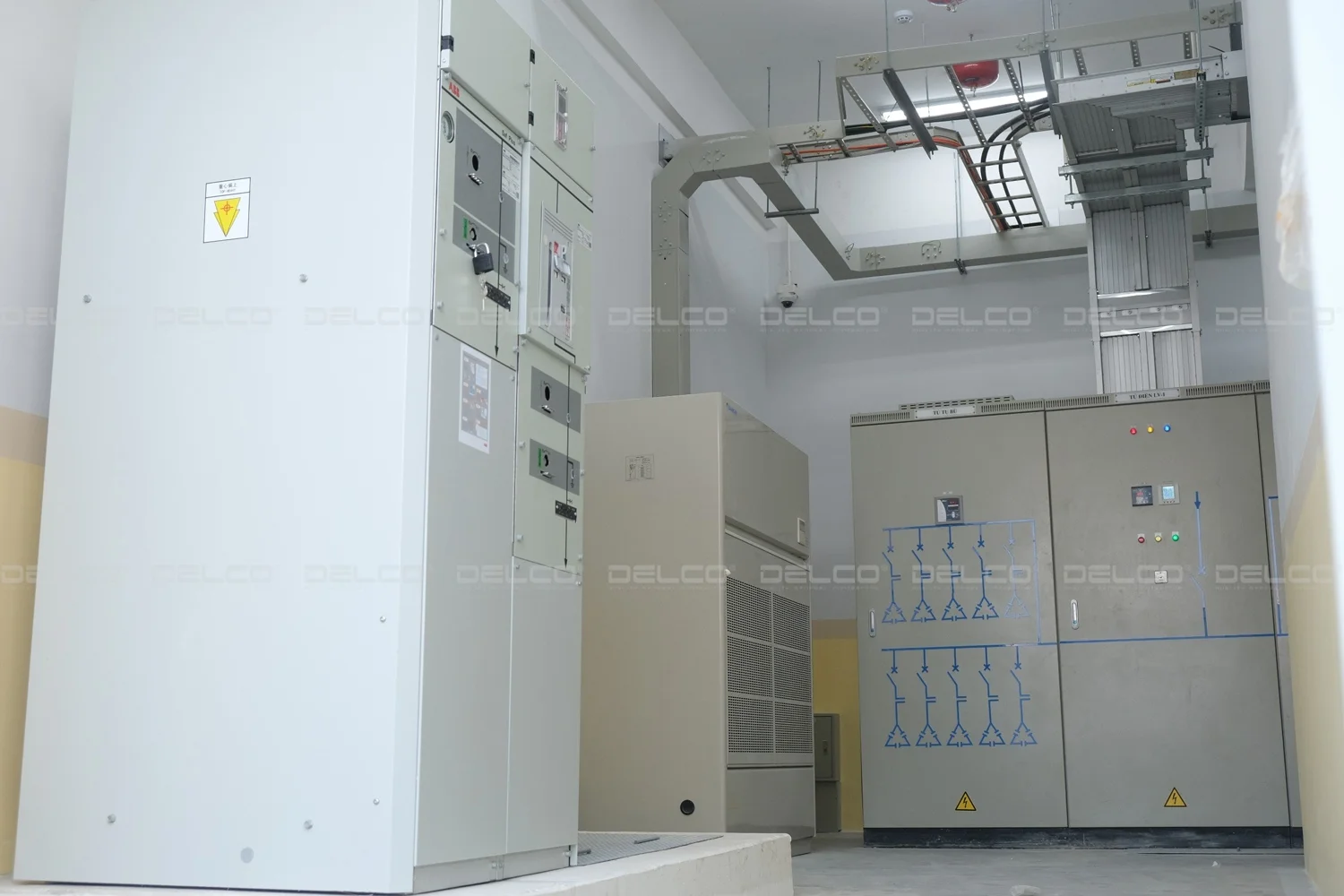

The medium voltage electrical cabinet at the DORCO Living Vina factory, where DELCO works the General Contractor, was calculated and designed for easy expansion in future stages.
Choosing the HVAC system suitable for the production characteristic
Each industry has different requirements for the HVAC system, so the design team must tailor the system to suit each sector and production area. For instance, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, the HVAC system requires strict temperature and humidity controls to keep the environment stable and prevent mold, which can damage products. Therefore, the investor needs to consider ventilation directions as well as the load-bearing capacity of the floor to support fans and vents properly.
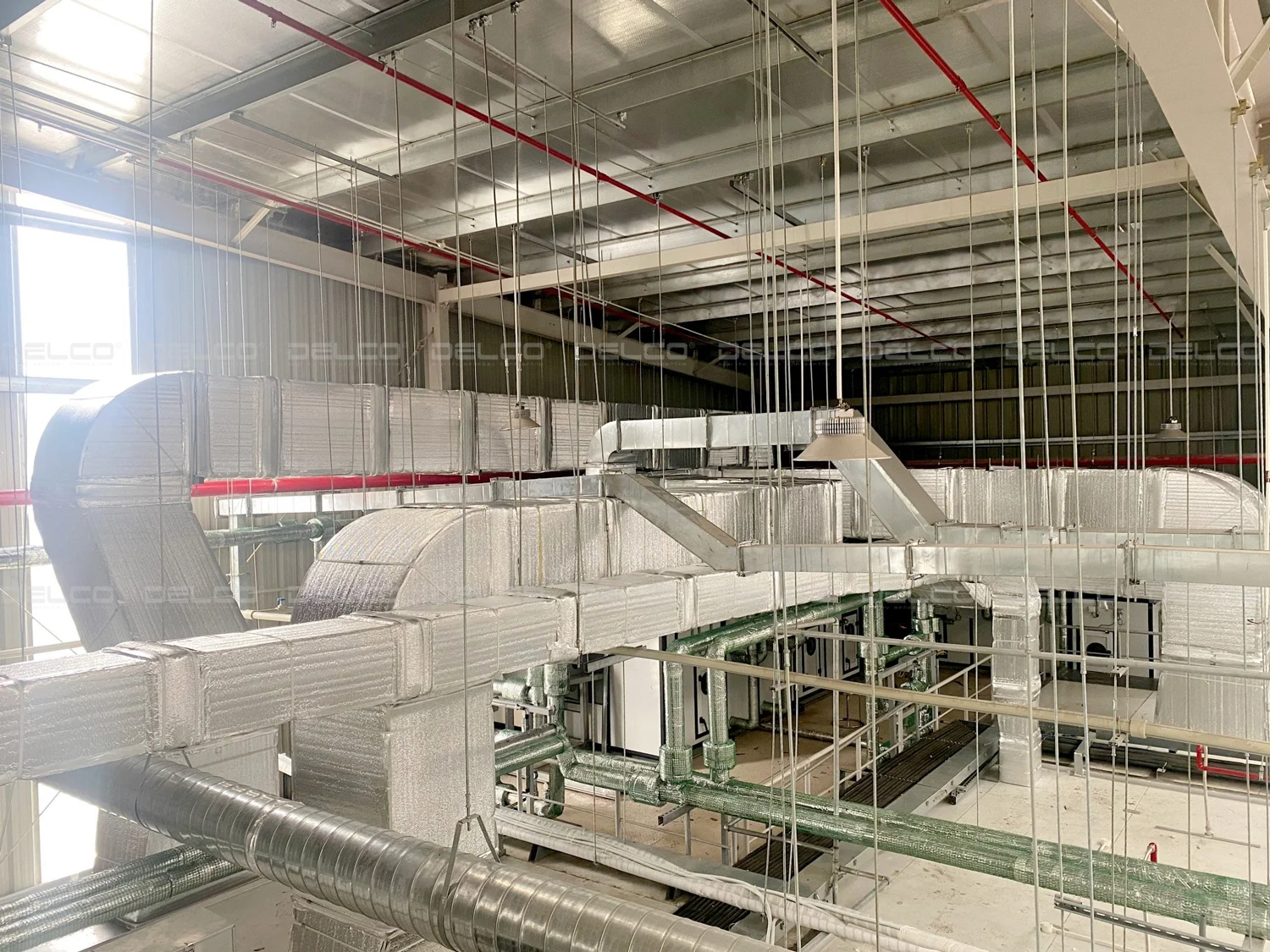

Additionally, based on the functionality of each area, the design team should calculate the heat load and choose an appropriate air conditioning system. The placement of air conditioning units must be strategically planned to ensure even cooling, maintaining stable temperatures and saving energy.
Designing fire protection systems complying with area functioning
When designing fire protection systems, the design team must strictly adhere to regulations outlined in QCVN 06:2021/BXD and Circular 02:2021/TT-BXD of Vietnam. The fire protection system must operate effectively and be suitable for the specific functions of each production area. For example, in chemical manufacturing plants, storage and handling areas for flammable materials require specialized fire suppression systems, such as foam, powder, or gas extinguishing systems, and stringent smoke extraction systems depending on the workshop area. Ventilation systems must ensure that chemical vapor concentrations are kept below 10% of the lower explosive limit.
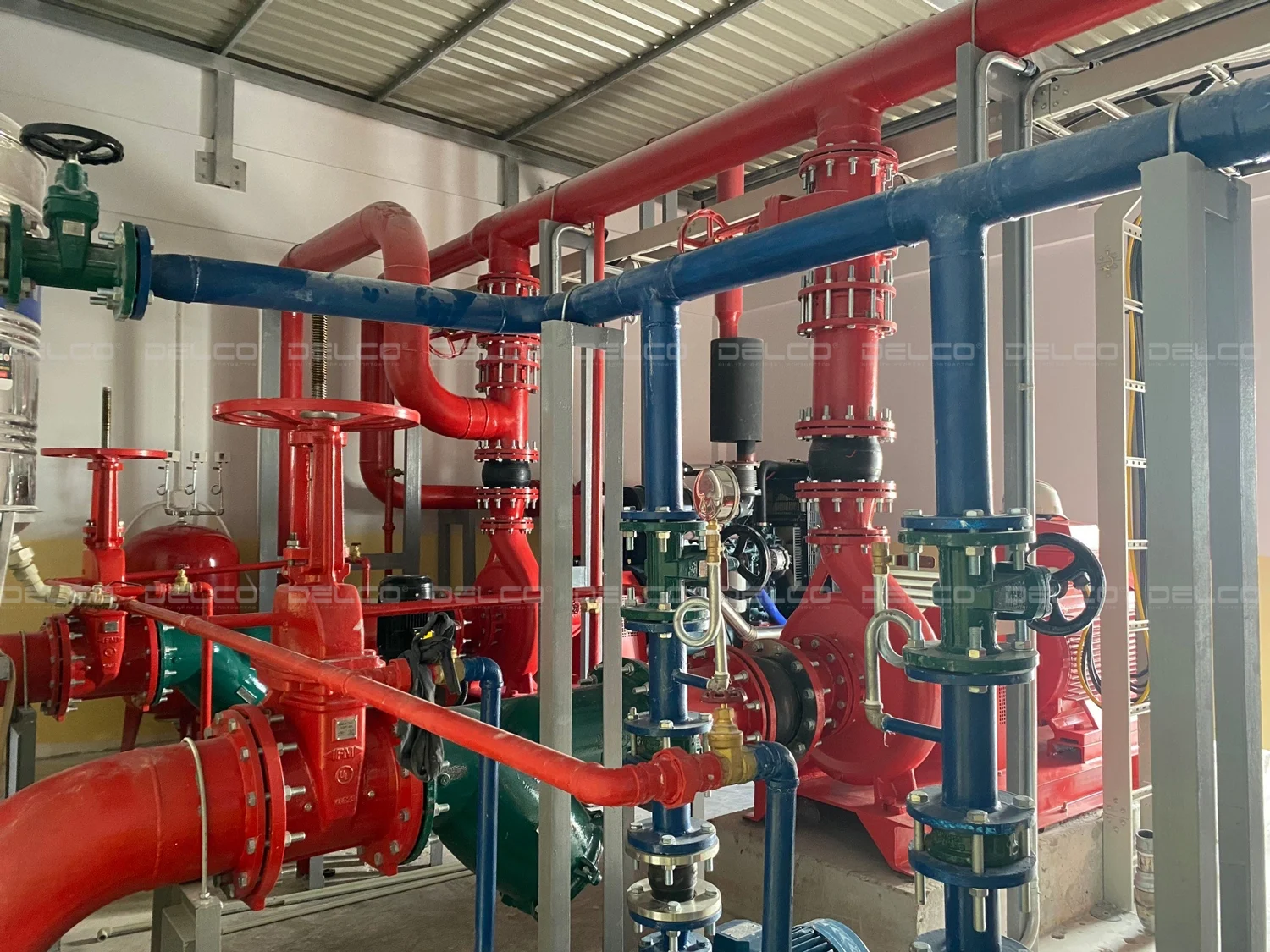

For electrical rooms or server rooms, water-based fire suppression systems are not allowed; instead, use systems like FM200, CO2, or nitrogen. In factories using water in the production process, such as stone powder manufacturing or fabric dyeing, the high humidity environment poses a lower fire risk, thus the fire protection design requirements are less stringent.
Furthermore, to avoid unnecessary risks, the contractor must prevent the spread of smoke and fire between areas within the workshop. Items with similar fire properties and extinguishing methods should be grouped together. Firefighting equipment should be placed in accessible locations, with hose spacing meeting technical fire protection standards, and escape routes should be clear to ensure quick and safe evacuation.
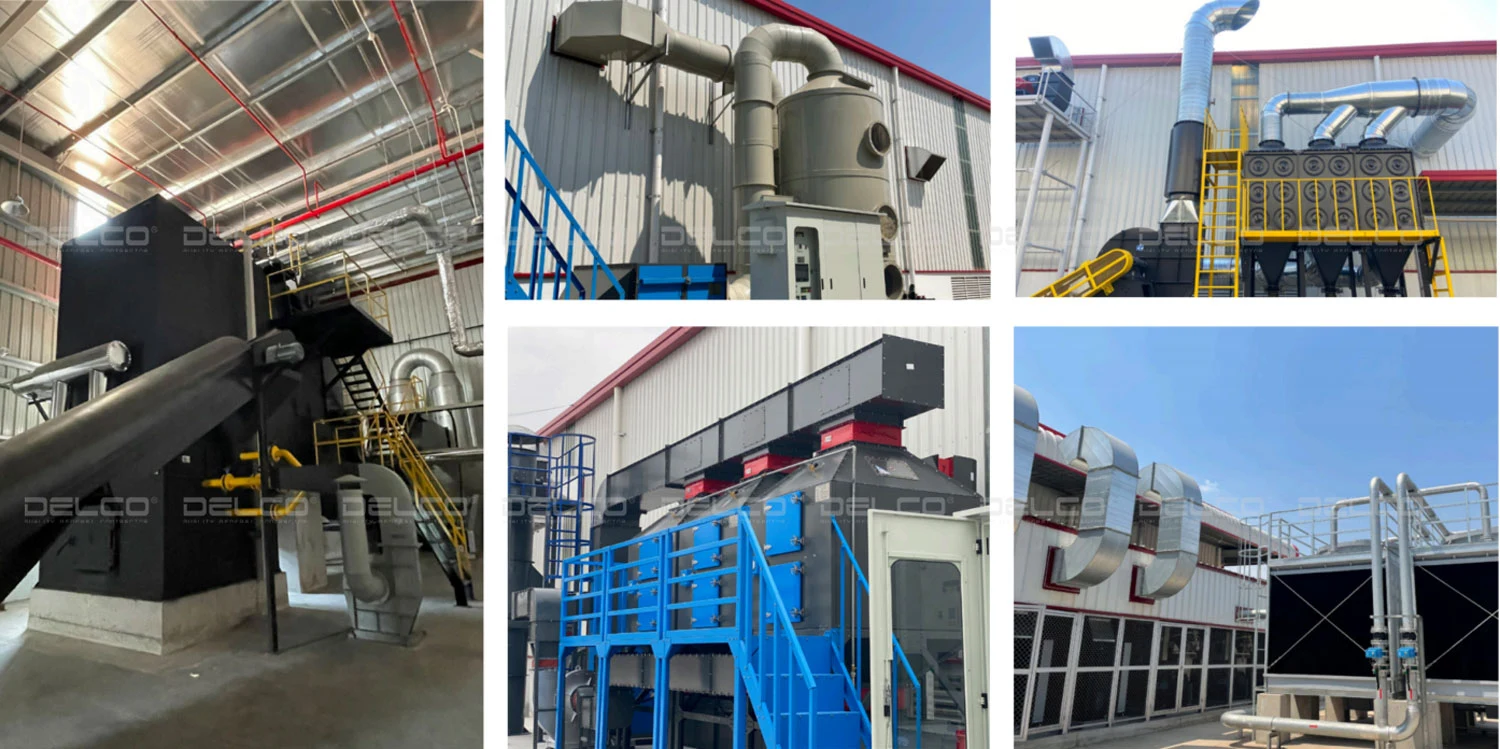
Designing the environment treatment system suitable for the production line
The factory design team must work with the investor to collect specific and accurate information about the production line and the characteristics of the factory’s wastewater. This helps to design a wastewater treatment system with appropriate area and treatment capacity. Investors can choose between biological treatment methods or chemical treatments based on the type of production and their budget.
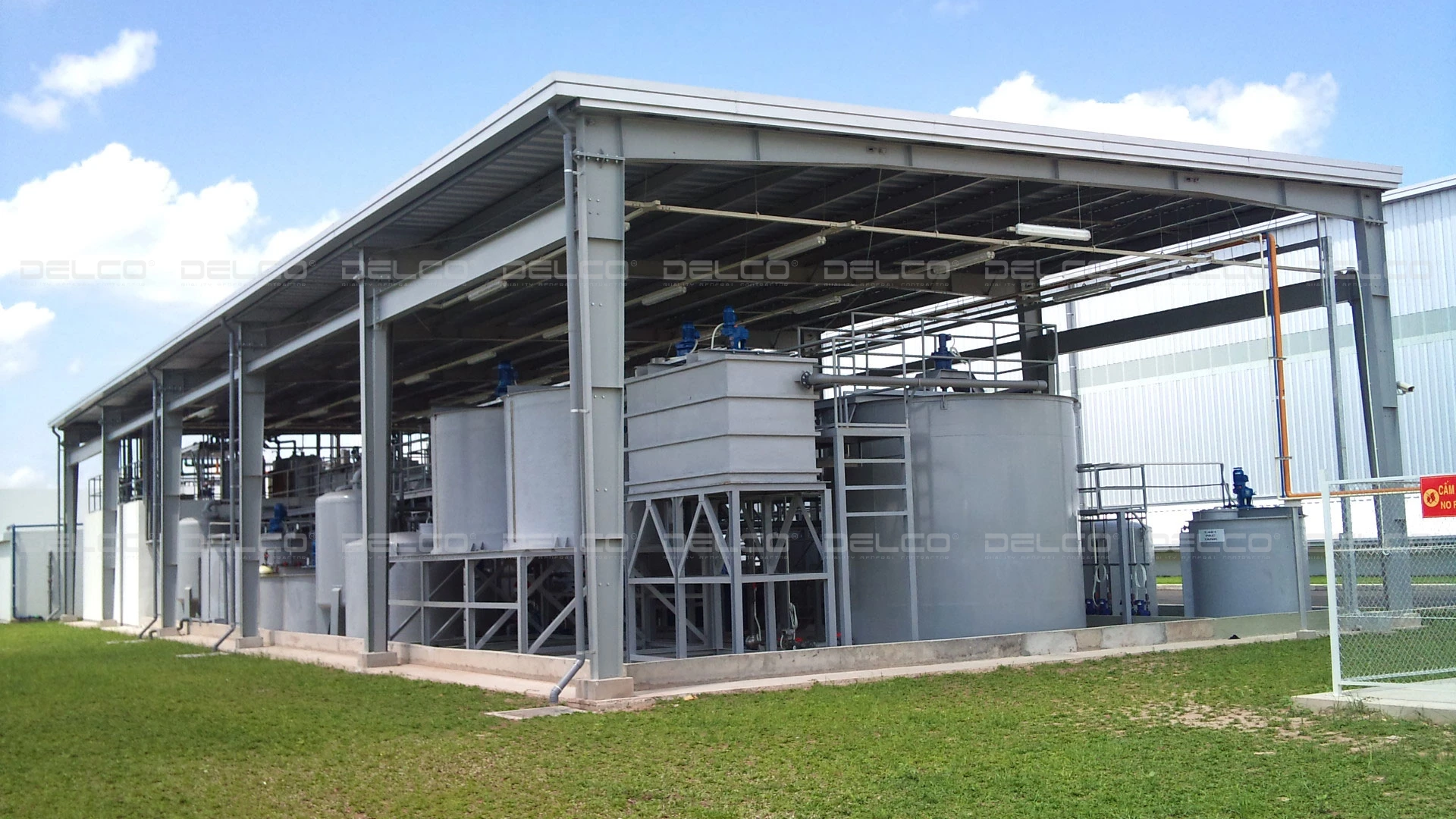

During operation, the factory may also need odor and dust treatment systems, depending on the production line. For factories with minimal wastewater and solid waste, businesses can collaborate with environmental contractors /partners for collection or choose to build advanced wastewater treatment technologies to recycle water. thereby saving operational costs.
See more: Factory office design ideas and trends 2024
See more: Smart Factory Trends in Vietnam