HVAC systems are among the largest energy consumers in industrial factories. Implementing the following four energy-saving solutions for HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy and operational costs for factories.
Optimized HVAC system design
Designing an HVAC system involves critical stages such as heat load calculation, equipment selection, ductwork design, ventilation system planning, and resolving pipe and structural conflicts. A well-designed system not only optimizes equipment costs but also reduces installation expenses and energy consumption during operation. Investors can evaluate and optimize HVAC system designs based on the following criteria:
- Selecting appropriate equipment: Careful research and precise calculation of HVAC system capacity are crucial to selecting the appropriate equipment and devices. Insufficient capacity results in extended operation times for air conditioning units to achieve the desired temperature, leading to higher electricity consumption and reduced equipment lifespan. Conversely, oversized capacity also wastes energy unnecessarily.
- Rational zoning of cooling areas: Dividing cooling zones based on actual usage needs enables better system design and equipment selection, avoiding energy waste in infrequently used areas.
- Optimizing ductwork design: An optimal ductwork layout with minimal bends reduces pressure loss and friction. This minimizes the load on fans and compressors while saving material and installation costs.
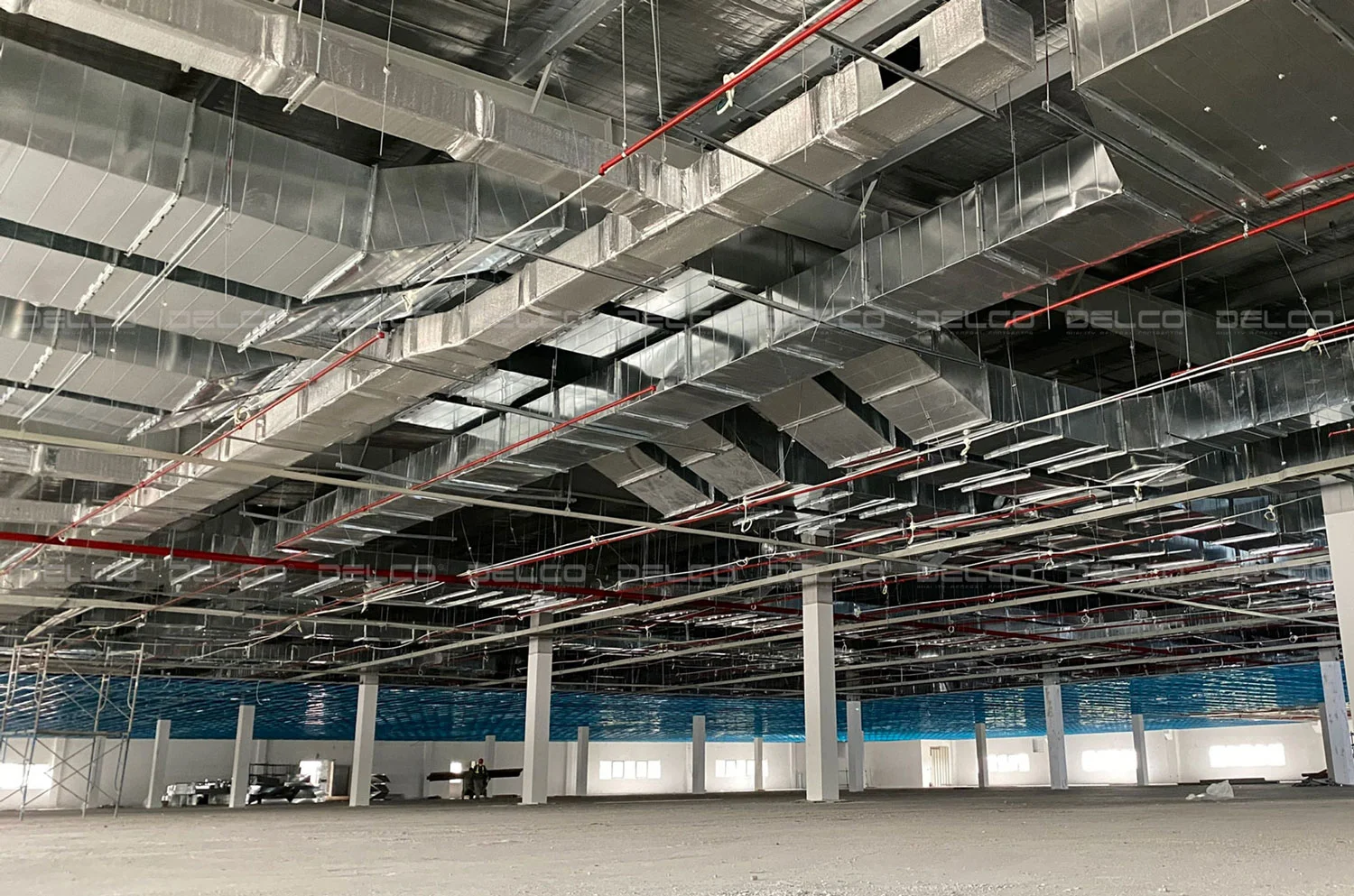

Optimized HVAC ductwork design reduces material costs, installation expenses, and operational energy consumption.
Using Thermal Insulation Materials
Thermal insulation materials help maintain stable temperatures in factories by minimizing heat loss during winter and preventing external heat intrusion during summer. A well-insulated factory reduces heat loss, thereby reducing the load on HVAC systems and effectively saving energy.
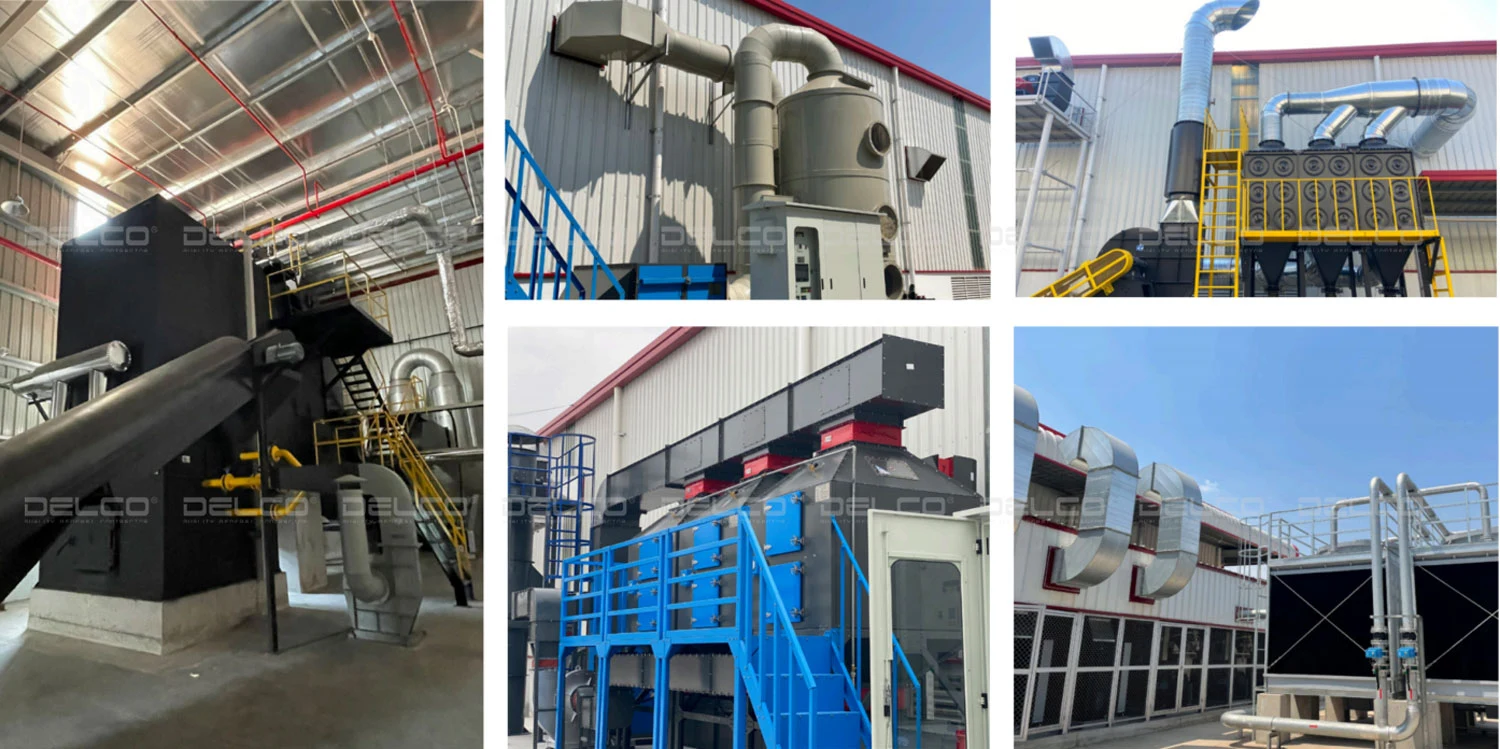
Utilizing Effective Insulation Materials: Materials such as insulated panels, thermal roofing, fiberglass, or heat-resistant paint can reduce heat transfer through the roof and walls of factories, easing the burden on HVAC systems.
Insulating Doors and Windows: Installing insulated glass windows or sun-blocking curtains can lower indoor temperatures, thereby reducing cooling demands for both factory and office spaces.
Smart Lighting Design: Many factories use light-transmitting panels to enhance natural lighting. However, it is crucial to carefully calculate the placement and area of such panels to avoid prolonged direct exposure to intense sunlight during summer, which can lead to overheating.
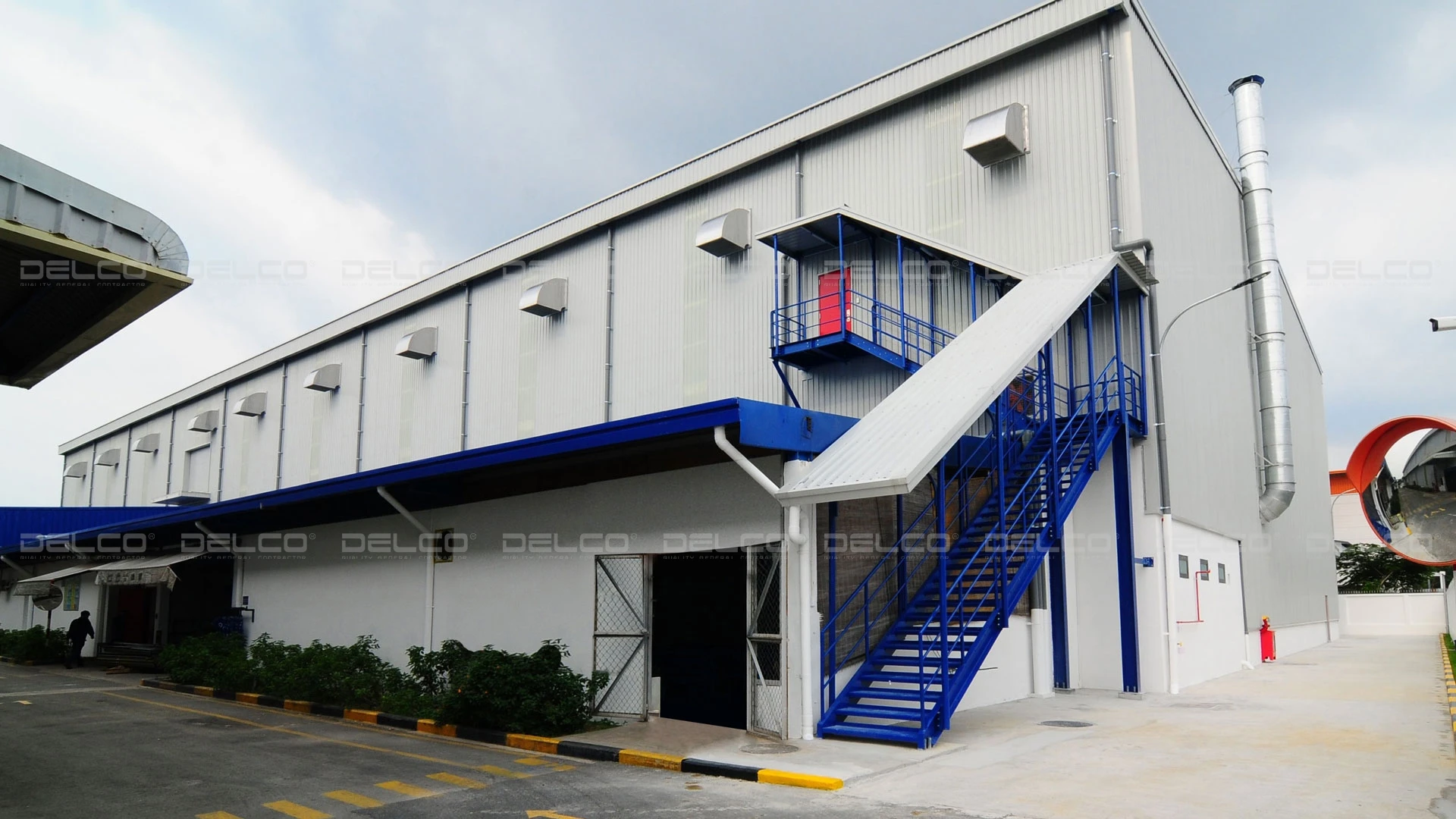

Effective thermal insulation materials help reduce heat loss, prevent overheating, and save energy for HVAC systems. Project designed and implemented by DELCO.
Applying Smart Control Technology
Integrating smart control technology involves the use of advanced devices and software, such as sensors, automated controllers, and intelligent management systems (EMS/BMS), to optimize the operation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. This solution reduces energy consumption by adjusting systems to actual needs, enhancing performance, and prolonging equipment lifespan.
Additionally, smart control technology enables businesses to monitor and analyze operational data, allowing timely adjustments and improvements.
- Intelligent Management Systems (BMS): BMS allows comprehensive monitoring and control of HVAC systems, including temperature, humidity, and air pressure in office or factory areas. This optimization improves energy efficiency, prevents under- or overperformance of equipment, saves energy, and extends the lifespan of devices.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Using VFDs in HVAC systems helps regulate the speed of pumps, fans, and compressors, ensuring energy-efficient and stable operation of HVAC equipment.
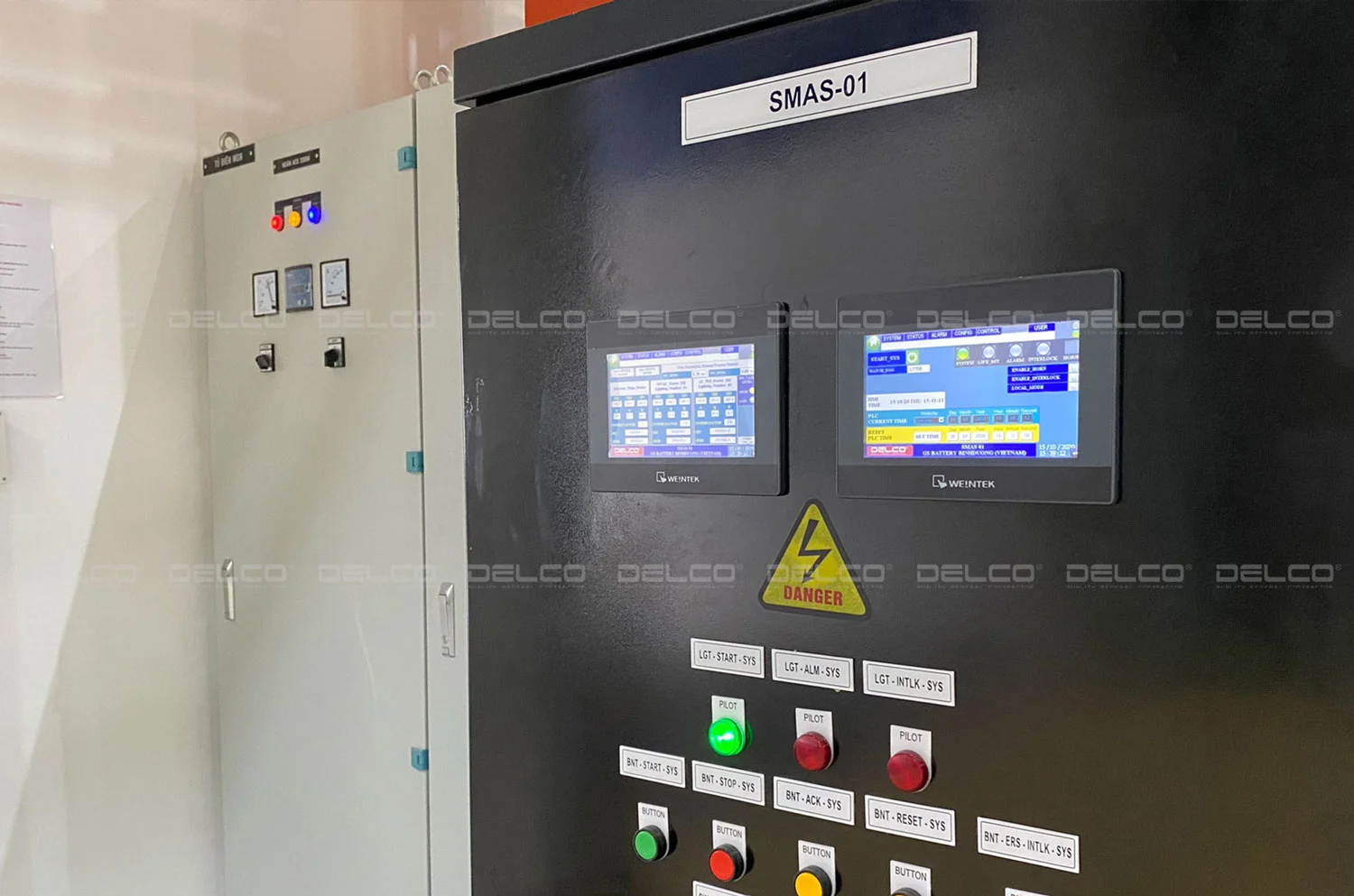

The BMS systems for factories, designed and implemented by DELCO.
Regular Maintenance of HVAC Systems
Maintaining HVAC systems involves inspecting, cleaning, and servicing system components to ensure efficient and stable operation. Key tasks include cleaning air filters, inspecting and cleaning ductwork, checking compressors and fans, monitoring refrigerant levels, and examining sensors or control devices. Regular maintenance helps sustain the performance of HVAC systems, ensures indoor air quality in factories, and promptly identifies and addresses potential issues such as equipment failures or energy-wasting thermal leaks.
- Cleaning Air Filters: Dirty filters reduce airflow, forcing the system to work harder to achieve desired performance, which leads to increased energy consumption.
- Inspecting and Maintaining Compressors: Ensuring compressors operate at their designed capacity prevents unnecessary energy wastage.
- Checking and Maintaining Duct Systems: Inspecting ductwork, copper pipes, and insulation helps detect and resolve issues like thermal leaks or condensation buildup, improving energy efficiency and extending the lifespan of HVAC equipment.
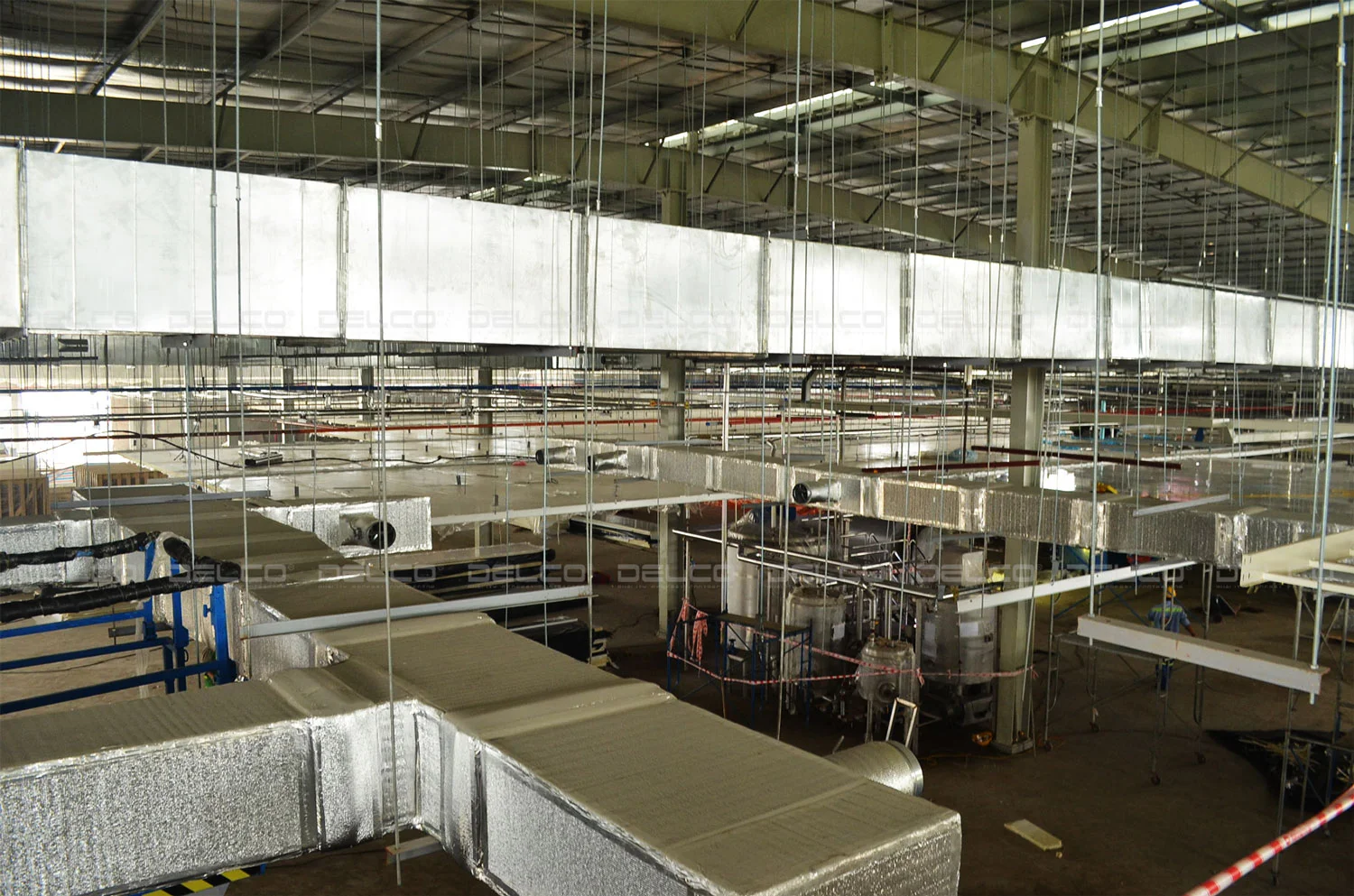

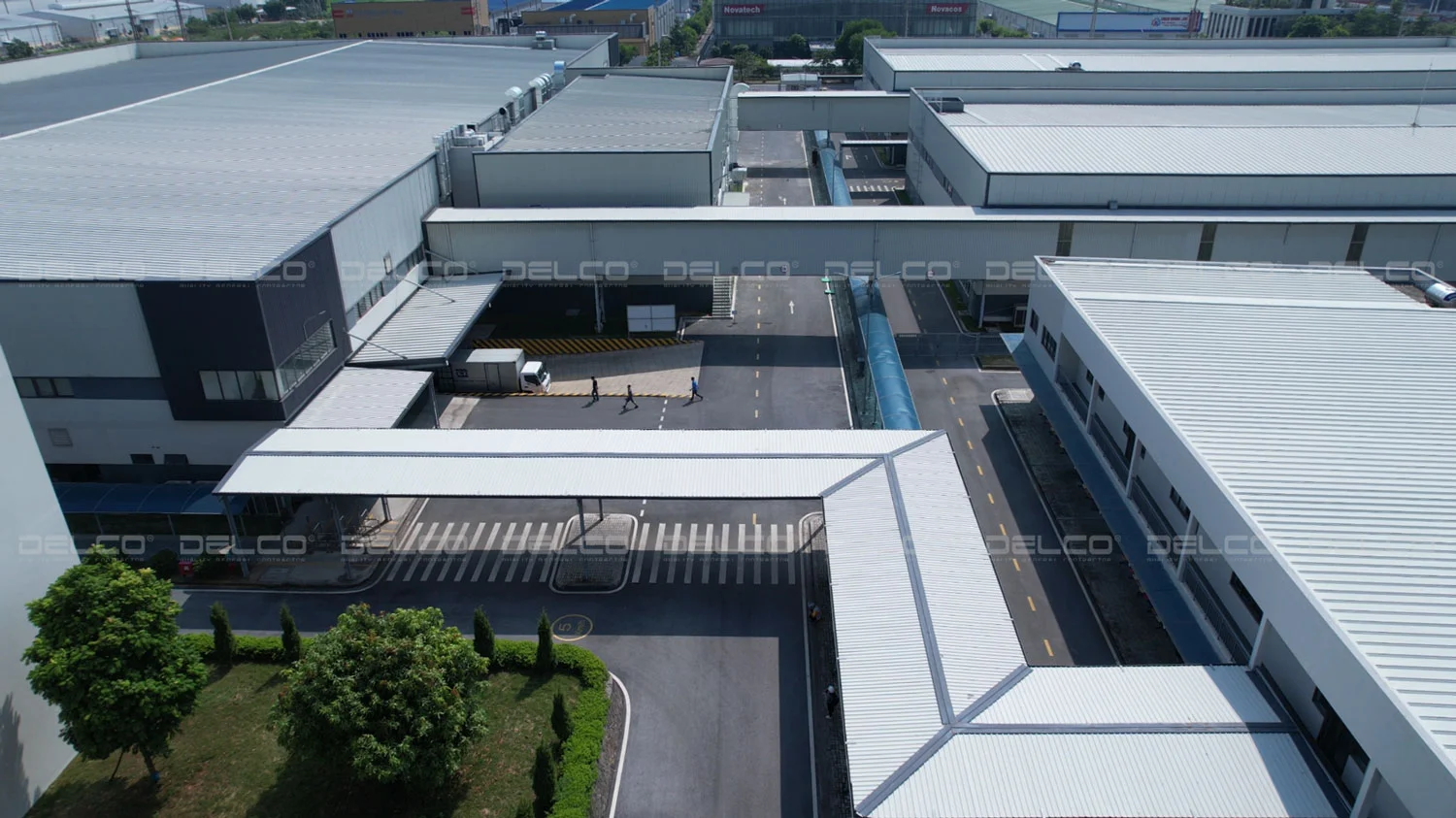
The industrial HVAC systems designed and implemented by DELCO
See also: HVAC technology trends in Vietnam in 2024