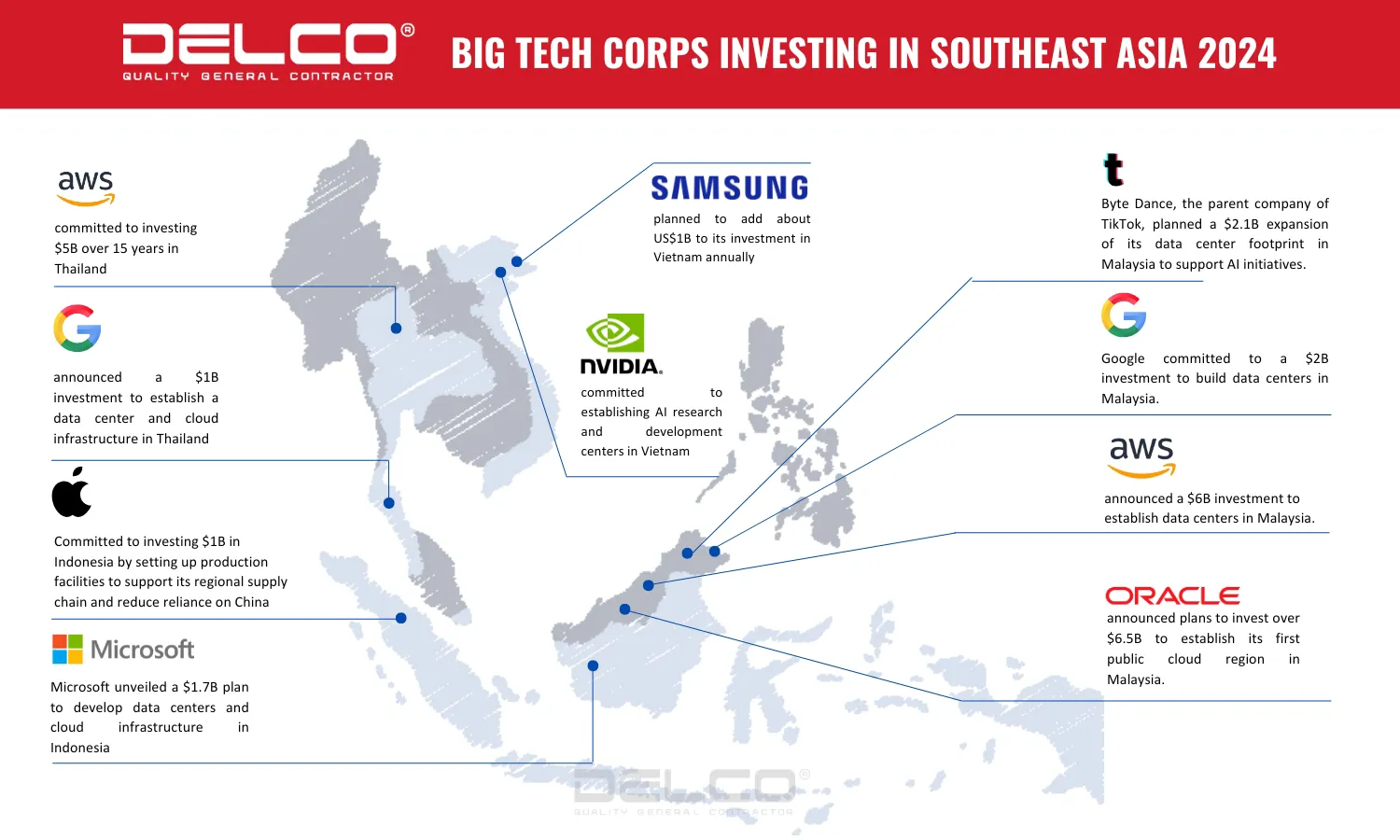
In recent years, Southeast Asia has emerged as a new global economic hub, particularly in high-tech sectors such as semiconductors, electronic components, and data centers. The re-election of President Donald Trump, along with his commitment to stricter tariff policies against China, has prompted major corporations like NVIDIA, Apple, and Google to redirect investments to Southeast Asia.
Reasons behind the flow of tech FDI to Southeast Asia
Amid global economic challenges following the pandemic, sluggish recovery, the risk of economic recession, and political conflicts in various countries, Southeast Asia stands out as a safe and promising investment destination for major U.S. tech corporations.
Escalating U.S.–China Trade War
The trade war between the U.S. and China, which began in 2018, continues to escalate as Donald Trump announced plans to impose tariffs of up to 60% on Chinese imports. In retaliation, the Chinese government has initiated measures such as investigations into NVIDIA and bans on exporting certain raw materials with military applications.

In this context, many tech corporations are shifting production to Southeast Asian countries to reduce their dependence on China. Recently, NVIDIA signed a partnership agreement with the Vietnamese government to establish an AI research and development center to support chip manufacturing. Similarly, Apple is planning to relocate part of its production line to Indonesia to diversify its supply chain.
Political instability in Europe and the Middle East
The Russia–Ukraine war has triggered an energy crisis in Europe, causing fuel prices to soar and pushing several countries into economic recession. As a result, production and operating costs in the region have risen sharply, negatively impacting industries and exports.
Meanwhile, escalating tensions and complex political dynamics in the Middle East have affected global oil prices, increasing transportation and production costs. This situation has driven U.S. tech corporations to accelerate restructuring their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with unstable markets.
With its relatively stable political environment and rapidly growing economy, Southeast Asia has become an attractive destination for investors, especially major tech corporations.
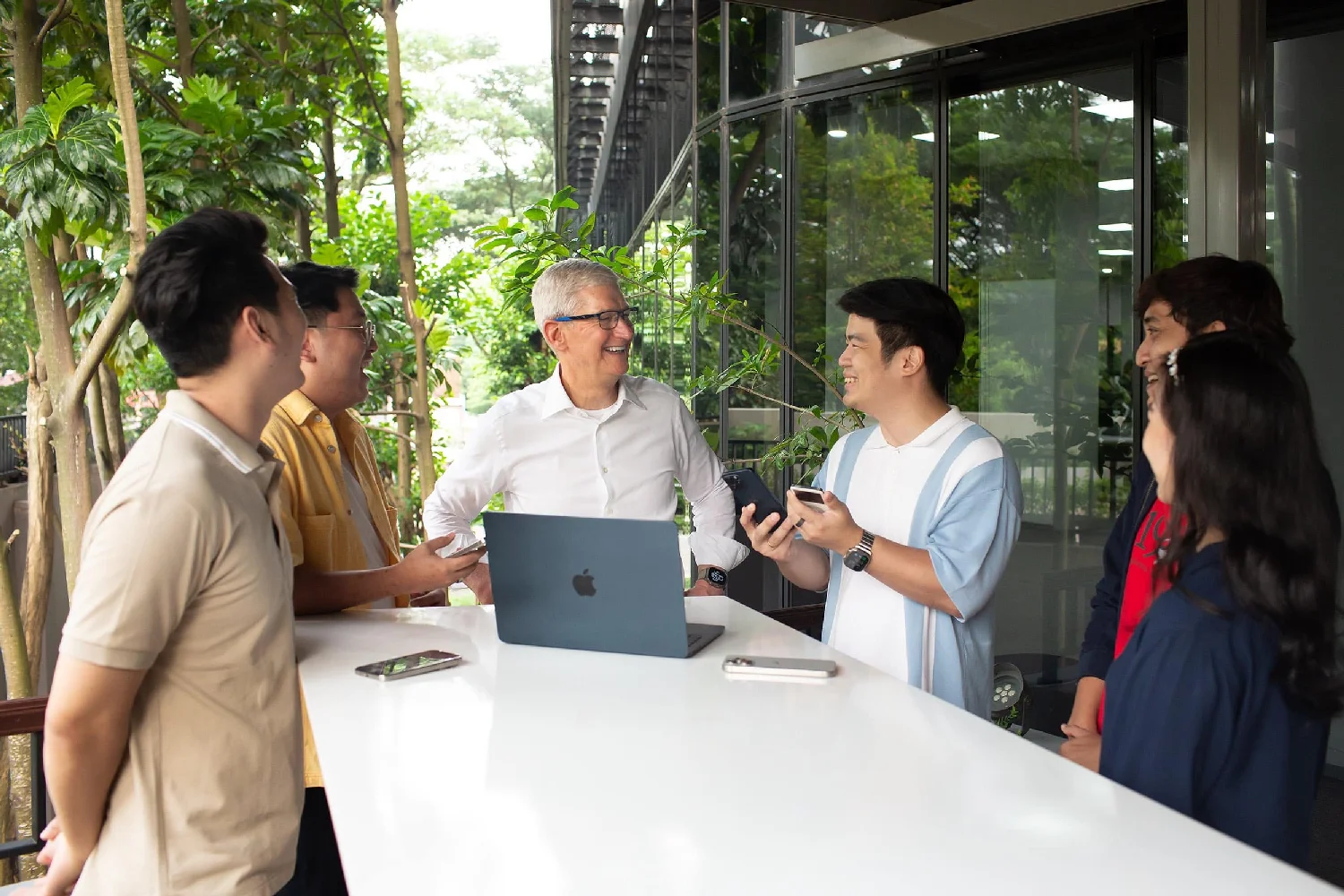

Apple CEO Tim Cook visits Singapore, Indonesia, and Vietnam in April 2024
Strategic Location and FDI Incentives in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia plays an important role in the global supply chain due to its strategic location connecting major markets such as Asia, Europe, and North America. Additionally, countries in the region, including Vietnam, Indonesia, Thailand, and Myanmar, have implemented attractive FDI incentive policies, creating favorable investment environments for foreign enterprises.
Vietnam has implemented numerous tax incentives for FDI businesses, such as corporate income tax (CIT) exemptions for the first two to four years, a 50% CIT reduction for the next four to nine years, exemptions on import-export taxes, and land rent waivers for up to five years. Similarly, Indonesia offers investment incentive programs such as tax holidays ranging from five to twenty years and land leases for up to 95 years. Thailand provides CIT and import-export tax exemptions for three to eight years for FDI projects involving high technology and those that add value to the local economy. These incentives have helped Southeast Asian nations attract capital from global corporations.

NVIDIA signs a partnership with the Vietnamese government for AI R&D center development
In addition, major trade agreements such as the RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) and CPTPP (Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership) have reduced costs and streamlined export-import procedures between ASEAN countries and partners across the Asia-Pacific region, including Japan, South Korea, Canada, Brunei, Australia, New Zealand, Mexico, and Chile.
See also: Tax incentives for FDI businesses in Vietnam
See also: List of Vietnam’s active FTA
Opportunities and Challenges for ASEAN in the Trump 2.0 Era
Economic Growth Opportunities and Political Benefits
The re-election of President Donald Trump may bring both economic growth opportunities and political benefits to ASEAN countries. Experts suggest that nations such as the Philippines, Brunei, Malaysia, and Indonesia view Trump’s return as a potential counterbalance to China’s ambitions in the South China Sea. Economically, many believe that Southeast Asian countries will benefit from the “China+1” strategy, where FDI—particularly in technology—shifts from China to neighboring countries like Vietnam and Indonesia, mirroring trends from Trump’s first term.
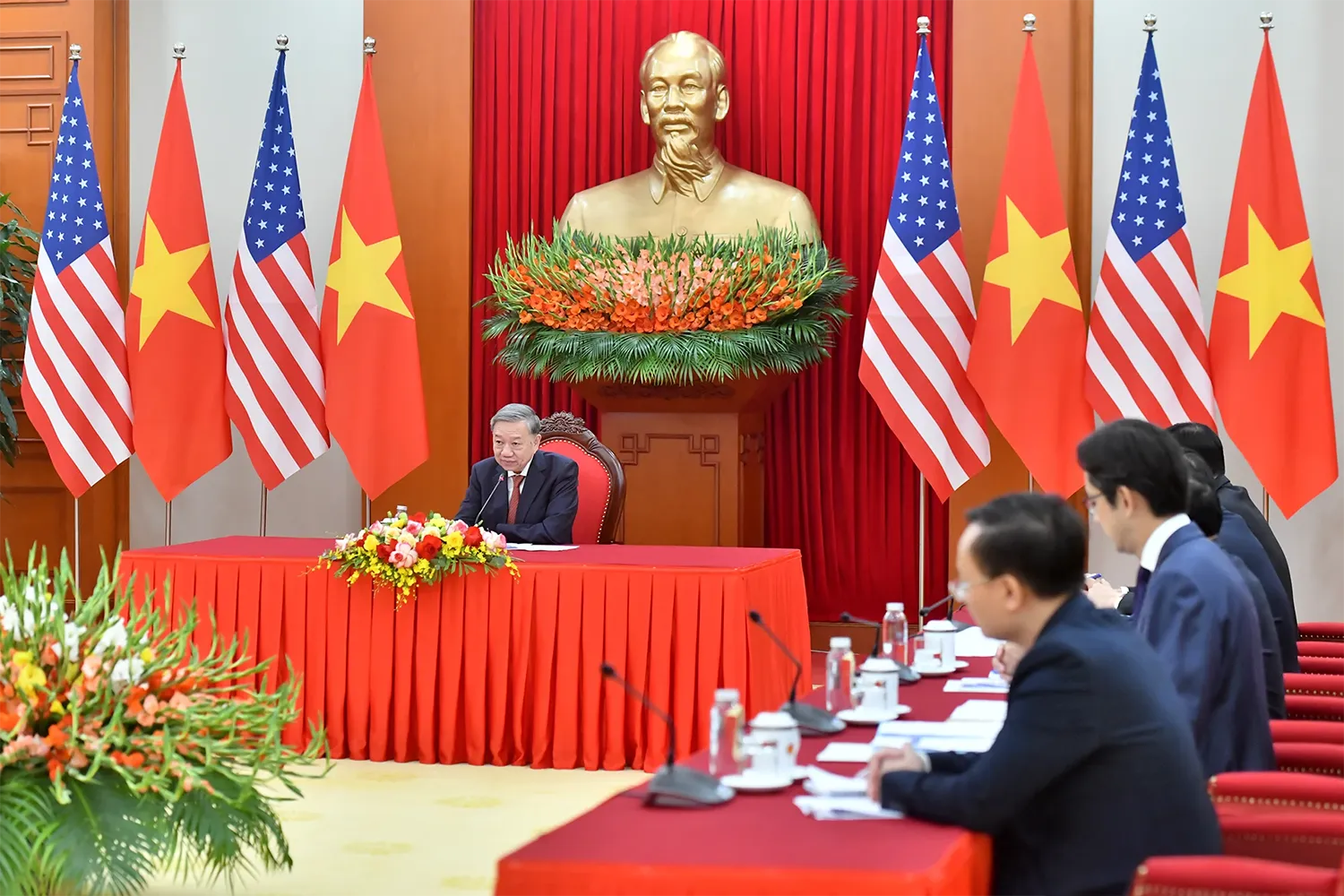

Just days after his re-election, President Donald Trump held a phone call with Vietnam’s General Secretary Tô Lâm to discuss economic, trade, and investment relations. This demonstrates Trump’s significant interest in Vietnam specifically and Southeast Asia as a whole.
Concerns Over Tariffs and Supply Chain Disruptions
Tariff Challenges
Alongside significant economic development opportunities, the ASEAN region faces challenges related to tariffs and supply chain disruptions stemming from economic policies in the Trump 2.0 era. During his 2024 campaign, President Donald Trump announced plans to implement aggressive tariff policies to reduce the trade deficit, revive domestic manufacturing, and decrease reliance on foreign suppliers. These policies may impact exports from ASEAN countries—currently the fourth-largest trading partner of the U.S.—particularly in key sectors such as textiles, automobiles, and electronics.
Concerns About Supply Chain Disruptions Due to China’s Retaliation
It is undeniable that Southeast Asian nations remain heavily influenced by China, both economically and politically. Therefore, escalating U.S.–China tensions during this period could present diplomatic and trade challenges for the region. Specific concerns include potential declines in import-export volumes of goods and raw materials to and from China, as well as supply chain disruptions in industries such as textiles, electrical equipment, machinery, electronics, and computers.
Predicted Trends in Tech FDI Growth in Southeast Asia
Major Tech Corporations Continue Heavy Investments
Large corporations are expected to sustain strong investment in Southeast Asia to leverage its strategic location and favorable business environment. NVIDIA has signed an agreement with the Vietnamese government to establish an Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Center to support the production of advanced chips, catering to the growing demand in the high-tech sector. Similarly, Google has announced plans to build a data center and cloud computing infrastructure in Thailand, with an investment of $1 billion to meet the region’s increasing digitalization needs.

Sustainable Investment and Green Technology
In addition to boosting production and infrastructure, future investment trends will prioritize sustainable projects and green technology. Investors are increasingly focused on renewable energy and integrating carbon-reduction solutions to align with global emission reduction and sustainable development goals.
Strengthening Regional Cooperation
Southeast Asia is expected to enhance ASEAN’s coordination role to promote economic collaboration and develop regional supply chains. Countries such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and Thailand are closely collaborating to strengthen supply chains for electronic components, creating a competitive edge over other regions worldwide. This not only fosters greater economic integration but also solidifies Southeast Asia’s position as a new economic and technological hub on the global map.
— This article is written by the content team at DELCO® Construction. Copyright for articles on the delco-construction.com website belongs to DELCO® Construction. Please do not copy or edit any content without written consent from DELCO®. —
See also: Frequently asked questions about foreign investment in Vietnam
See also: List of billion-dollar FDI projects in Vietnam in 2024






