Steel structures are a popular choice for industrial factory construction due to their fast installation and high load-bearing capacity. Below is a summary of important considerations during the steel structure erection process, along with key acceptance criteria for contractors and investors to reference.
1. Site survey and design
In the survey and design phase, understanding the investor’s requirements plays a crucial role. Investors should provide complete information regarding the factory’s scale, type of production, column spacing requirements, internal space layout, crane systems, and load capacity. At the same time, the design team will assess the site’s geological conditions and surrounding infrastructure to propose suitable structural and foundation solutions — such as whether to use shallow or deep foundations, how to connect steel columns to the foundation, and what structural cross-section is most efficient. Working with an experienced design consultant helps ensure structural safety, load-bearing performance, and cost-effectiveness.
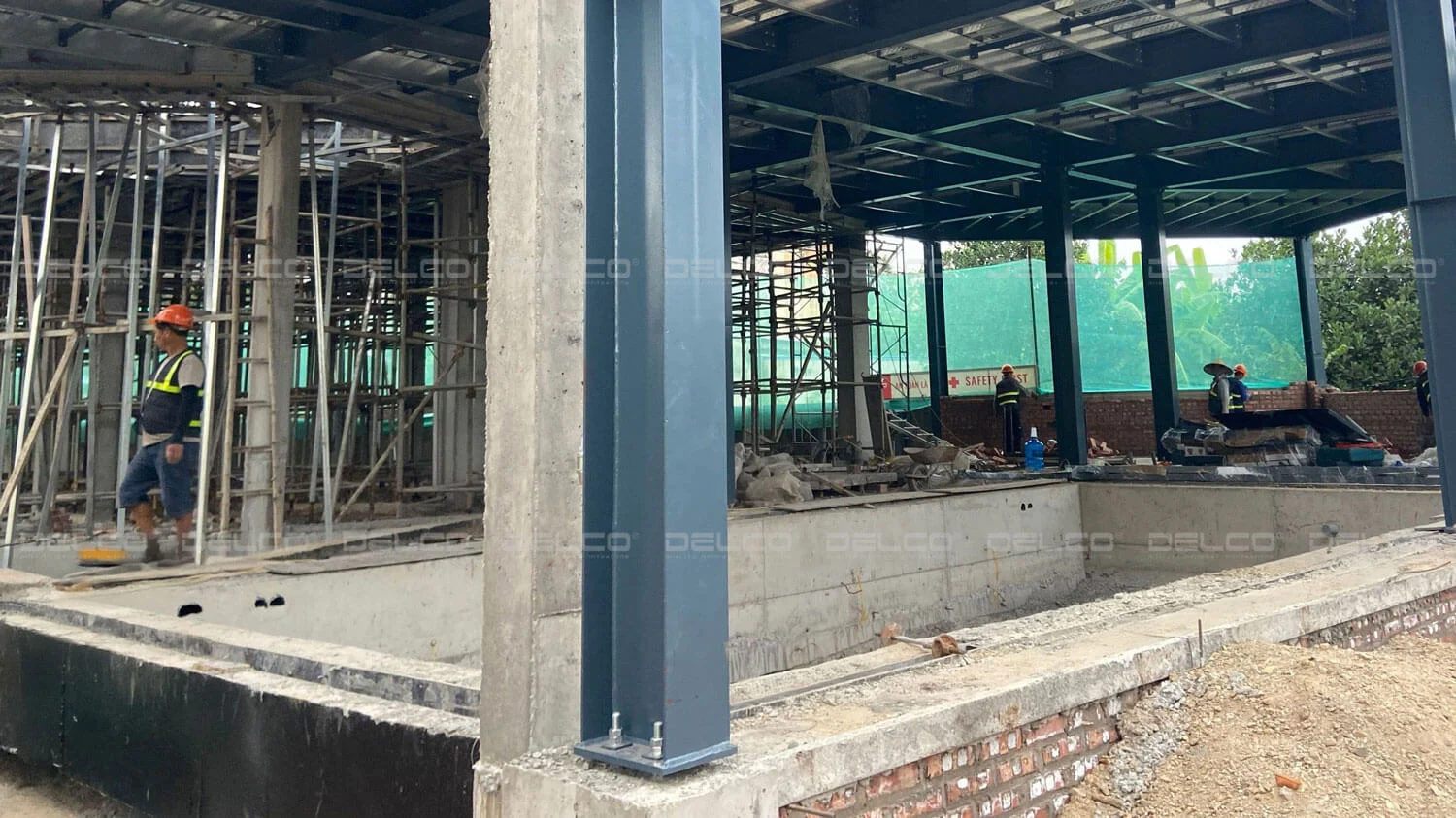

DELCO applied a pinned base connection for steel columns at the Nguyen Quoc Office Building — a solution commonly used for factories without overhead cranes.
2. Structural steel fabrication at the factory
Steel components such as columns, trusses, bracing, and purlins are fabricated at the factory based on approved drawings. Before fabrication, the contractor must provide complete certificates of origin (CO) and certificates of quality (CQ) to verify the source and quality of the steel materials. The fabrication process includes cutting, welding, assembly, and surface finishing with anti-rust coatings or galvanization.
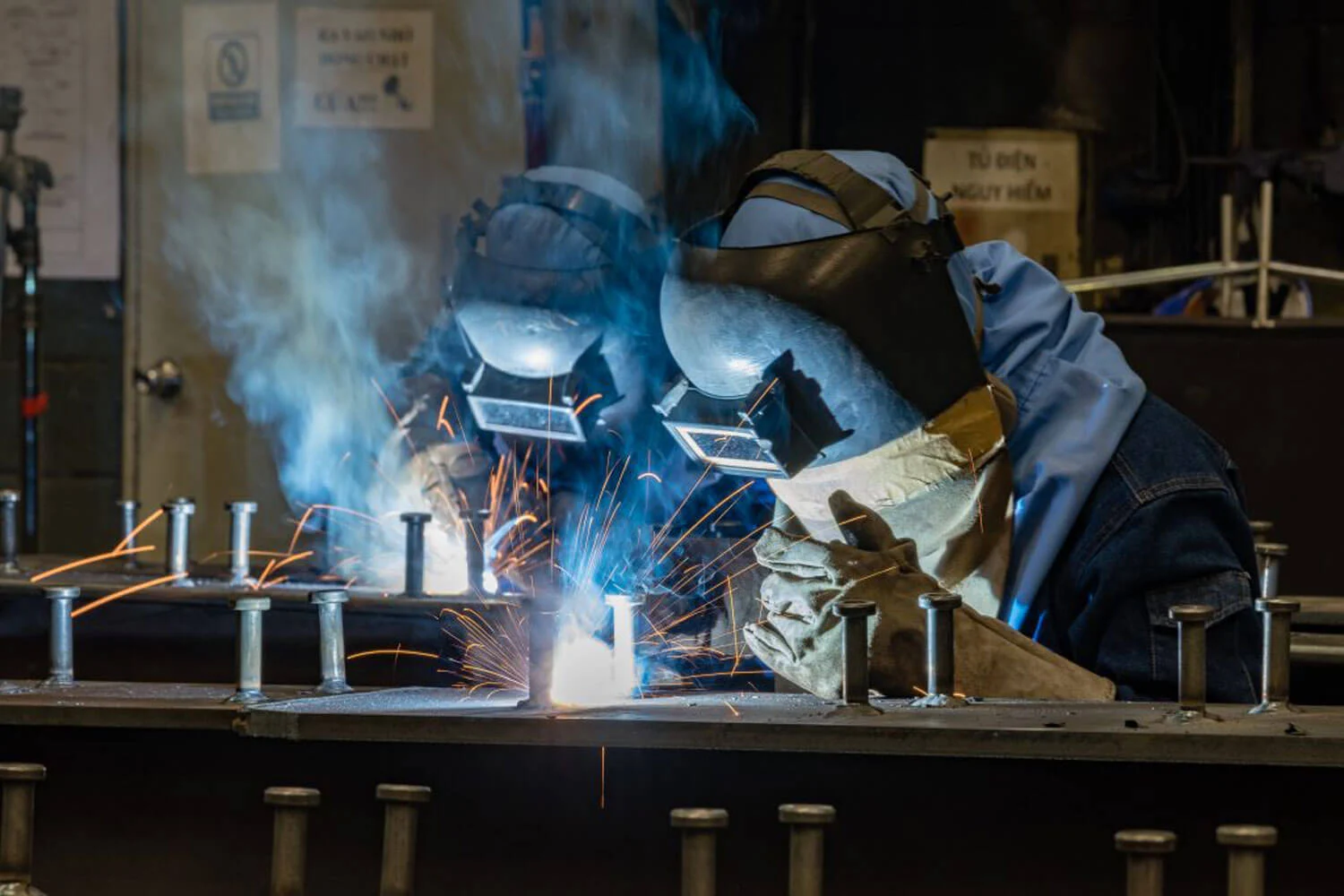

This stage directly affects the durability and lifespan of the project, so steel components must undergo quality checks and laboratory testing before being shipped to the site. The investor may also hire a supervision consultant or an independent inspection unit to conduct non-destructive tests — such as ultrasonic, penetrant, or magnetic particle testing — to detect hidden welding defects. Additionally, the contractor must provide complete quality documentation and acceptance reports for all components before transporting them to the construction site.
3. Foundation construction and anchor bolt installation
The foundation bears the entire load of the structure, so it must be constructed according to design specifications and in full compliance with reinforced concrete standards. Anchor bolts play a critical role in ensuring the stability and alignment accuracy during steel structure erection, so their installation must be strictly controlled.
Before installation, anchor bolts must be inspected and tested, with records verifying that they meet technical requirements. Additionally, the dimensions and shapes of the bolts must be checked to ensure they conform to the design specifications. During concrete pouring, the bolts must be positioned precisely as per the drawings, as they form the direct connection with the steel frame. Even minor misalignments can impact the verticality and overall stability of the entire structure.
4. Erection of the main frame
Steel structure erection can only proceed once the foundation has reached its required design strength. Structural components are lifted and installed in sequence — starting with the steel columns, then trusses, bracing systems, and purlins. Given the substantial weight of these components, the lifting and installation process must be carefully calculated and executed with strict safety measures in place.
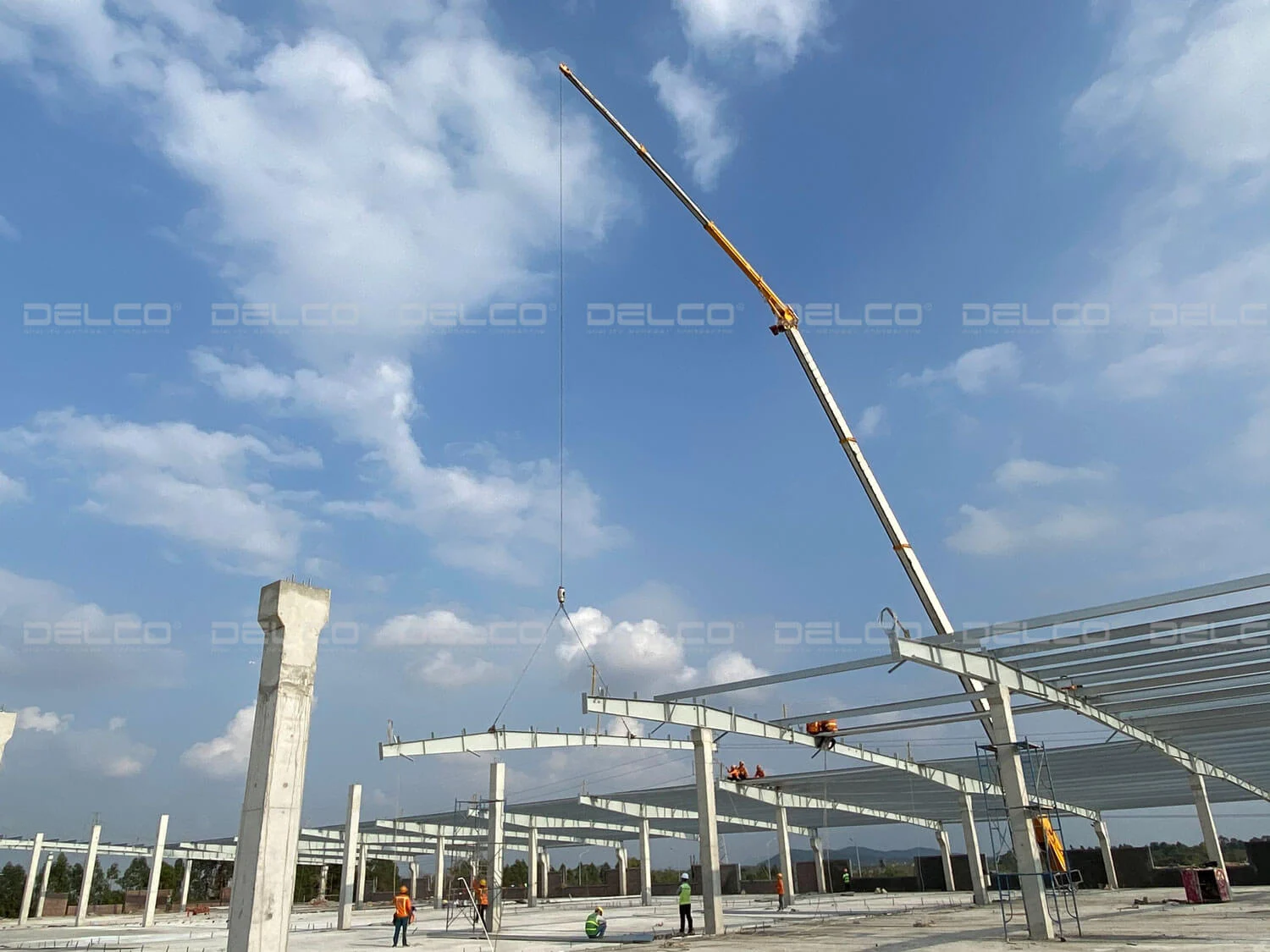

Steel structure erection at Power Plus Technology Factory, with DELCO as the Design & Build contractor, applying strict safety measures.
At this stage, investors should focus on the following key tasks:
- Verifying the vertical alignment and torsion of the frame after assembly
- Checking the tension of high-strength bolts using torque wrenches or specialized measuring tools
- Inspecting on-site welds (if any) through ultrasonic testing or other non-destructive testing (NDT) methods
Ultrasonic inspection and bolt tension testing are highly specialized tasks. To ensure objectivity and accuracy, investors may consider hiring a supervision consultant or an independent inspection agency.
5. Roof and cladding installation
Once the steel frame has been securely fixed and preliminarily approved, installation of cladding components — such as corrugated iron roof, insulation panels, corrugated iron walls or other materials will begin. The roofing system must comply with both technical standards and design requirements to withstand wind and storm loads. All joints must be watertight, leak-proof, and aesthetically pleasing. This stage also involves installing the roof drainage system, as well as thermal and sound insulation systems in a synchronized manner.
6. Final inspection and handover
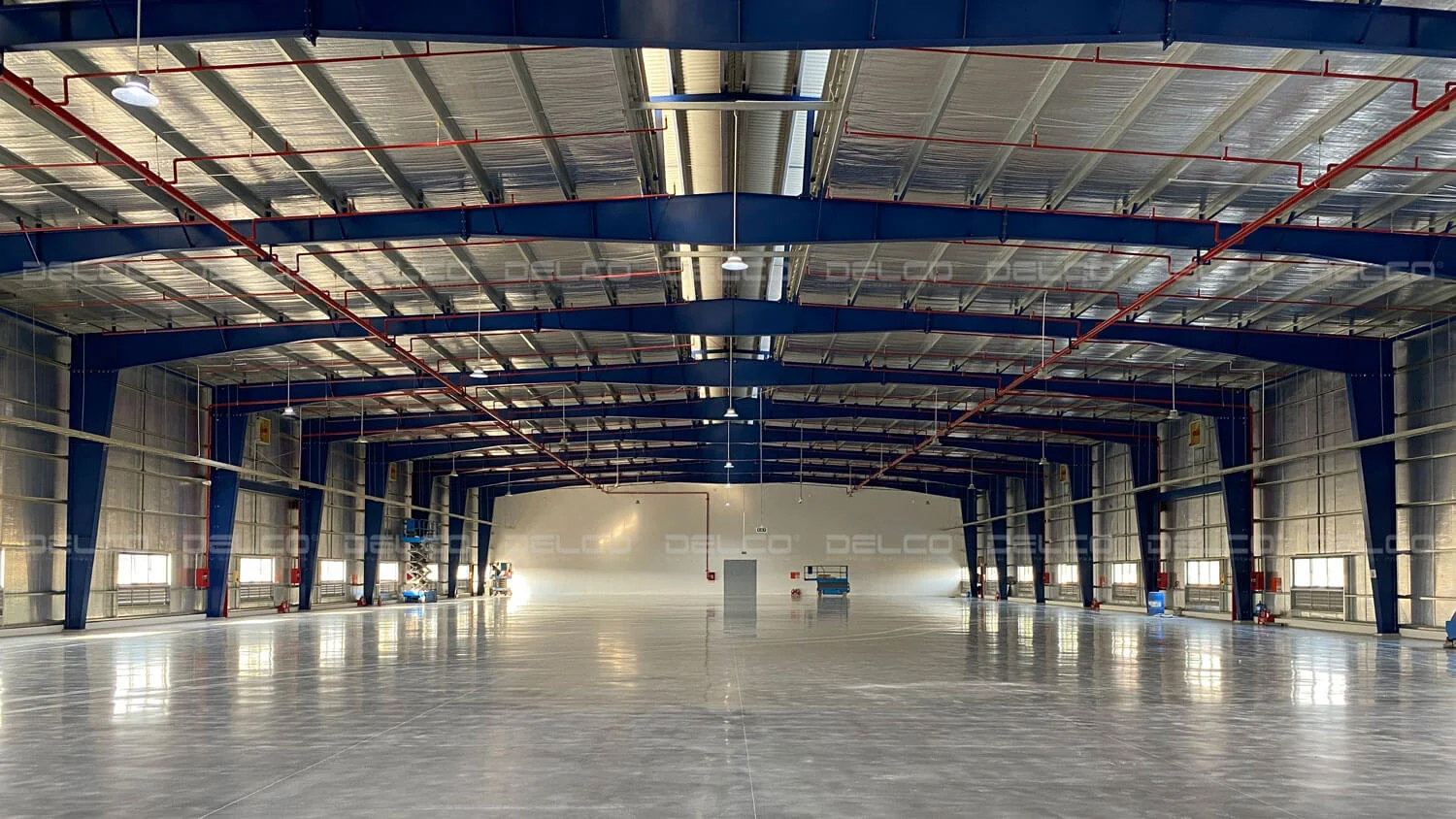

The investor and contractor conduct a comprehensive final inspection to detect and resolve any defects or inconsistencies that may not have been foreseen during the design and construction phases. In addition, the contractor is responsible for handing over all legal and technical documentation to the investor, including acceptance records for each work item, inspection reports for welds and bolts, as-built drawings, material quality certificates, etc. The project can only be handed over and put into operation once on-site acceptance meets steel structure standards and all documentation is complete.
See more: Steel structure factories vs. reinforced concrete factories comparison
See more: Pros and cons of steel structure factories