What legal and capital conditions do foreign investment in Vietnam need to meet, what are investment incentives,… The information below will help investors understand the procedures and be ready to participate in the Vietnamese market.
Why invest in Vietnam?
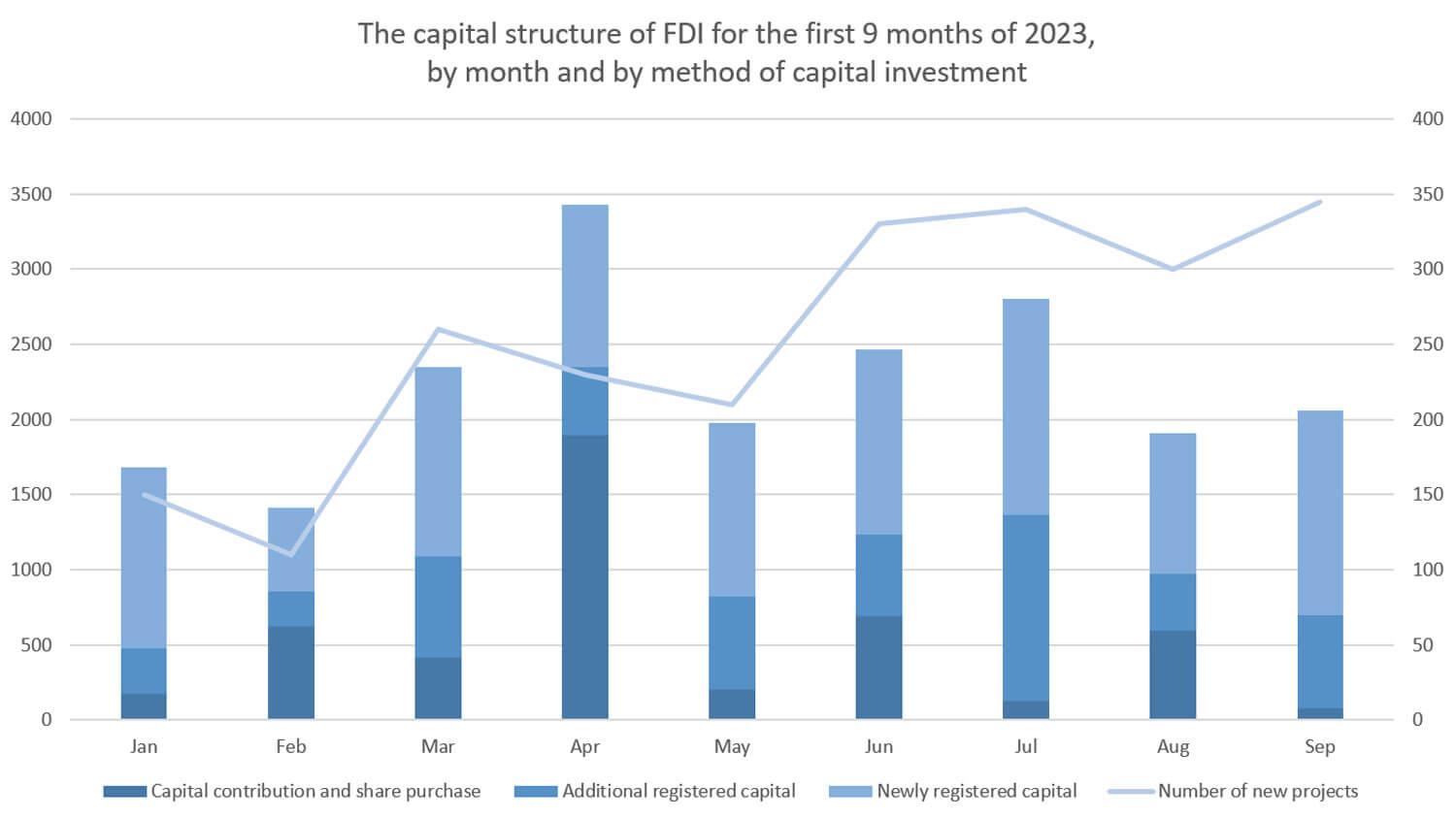
According to the Foreign Investment Agency (FIA), as of September 20, 2023, the total newly registered capital, adjusted and contributed capital for share purchases, and capital contributions of foreign investors reached nearly 20.21 billion USD, an increase of 7.7% over the same period.
Vietnam has been continuously recognized by world organizations for its political stability, positive economic growth, continuous improvement of the investment environment, and efforts to implement multilateral diplomacy. As of September 2019, Vietnam has participated in the negotiation and implementation of 17 free trade agreements (FTA). Besides, Vietnam has a favorable geographical location, potential consumption market, a population of 99.9 million people, a young and skilled labor force,… For foreign investors, Vietnam is a safe and attractive investment destination in a rapidly unstable, complex and unpredictable international context.
Foreign in Vietnam FAQs
What are the procedures and conditions of foreign investment in Vietnam?
In order to set up a business in Vietnam legally, foreign investors must meet the following conditions:
- Legal conditions: Foreign investors must complete business registration procedures and own necessary certificates. Some forms of business registration are popular with foreign investors in Vietnam such as establishment of 100% foreign -invested companies, joint venture companies, establishment of representative offices,…
- Capital conditions: Law of Vietnam stipulates the minimum capital for a number of conditional business sectors such as insurance, transportation… The different minimum capital levels depend on the scale and field of operation of the enterprises. For example: Real estate enterprises with 100% foreign investment must have a capital of at least 20 billion dong; The larger the scale of the factory, the greater the minimum capital.
- Other conditions: The investor has nationality(for individuals) or address of head office (for organizations) in the countries participating the WTO; Investment industries are not on the list of prohibited business or investments.
Procedures for establishing a foreign-invested company in Vietnam include the following basic steps:
- Investment registration:
- Investment Registration Office, Department of Planning and Investment where the enterprise is headquartered.
- Time: 15 – 20 days
- Business registration:
- At the Provincial Business Registration Office
- Time: 5 – 7 days
- Tax liability:
- Register for a tax code at the local tax authority
- Declare and pay license tax within 30 days since receiving the business registration certificate
- Declare annual taxes, pay value added tax, company income tax
- Register a bank account in Vietnam to accomplish financial transactions.
See more: Procedures for establishing a foreign-invested company in Vietnam (updated 2023)
What incentives do foreign-invested enterprises in Vietnam enjoy?
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT): Newly established manufacturing facilities are exempt from tax within the first 2 years, and a 50% reduction within the next 2 years. If they invest in fields, industries, and economic regions that receive investment incentives, they will enjoy lower tax rates than other projects. The maximum exemption period is 13 years (4 years for exemption, 9 years for reduction).
- Incentives on import and export taxes: Exemption from most import taxes on machinery, equipment, supplies and raw materials for production; Prioritize and encourage the export of processed goods (0% tax rate).
- Incentives on finance of land: Land rent reduction of up to 50% for projects in the field of investment incentives; Investment projects in areas having difficult socio-economic conditions; The enterprise’s land uses from 20% to 50% of its workers who are invalids and sick soldiers.
What types of tax rates apply to foreign investors in Vietnam?
In general, there are 4 common types of taxes, applicable to most business investment activities in Vietnam:
| Tax | Fees payable / Tax rate | Submission deadline |
| License fees (taxes). |
| No later than January 30 annually. |
| Value added tax (VAT) | The VAT rate schedule depends on the business sectors:
| For enterprises declaring monthly: The deadline for payment is the 20th day of the month following the month in which tax liability arises. For businesses declaring quarterly: The deadline for payment is the 30th or 31st (last day) of the first month of the quarter following the quarter in which tax liability arises. |
| Corporate income tax | The tax rate is 20% of total gross income. For oil and gas exploitation enterprises, the tax rate can be up to 32%-50%, for other rare resources exploitation enterprises it is 40%-50%… | Pay corporate income tax quarterly, the payment deadline is the 30th day of the first month of the following quarter. |
| Personal income tax | Personal income tax = Taxable income from salaries and wages x Tax rates Tax rates are calculated based on a partially progressive schedule. | No later than the last day of the 3rd month since the end of day of a year or a fiscal year for annual tax finalization dossiers; No later than the last day of the first month of a year or fiscal year for annual tax returns. |
In addition, it depends on specific business activities, maybe apply other taxes such as:
- Special consumption tax;
- Natural resources tax;
- Import Tax;
- Export tax;
- Environmental Protection tax.
- Non-agricultural land use tax
Localities attract foreign investment in Vietnam
Provinces and cities that have many advantages in attracting FDI in Vietnam include Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Bac Giang, Binh Duong, Hai Phong, Bac Ninh, Dong Nai,… These are localities that have invested in good infrastructure, stable human resources, efforts to reform administrative procedures and Active in investment promotion,…
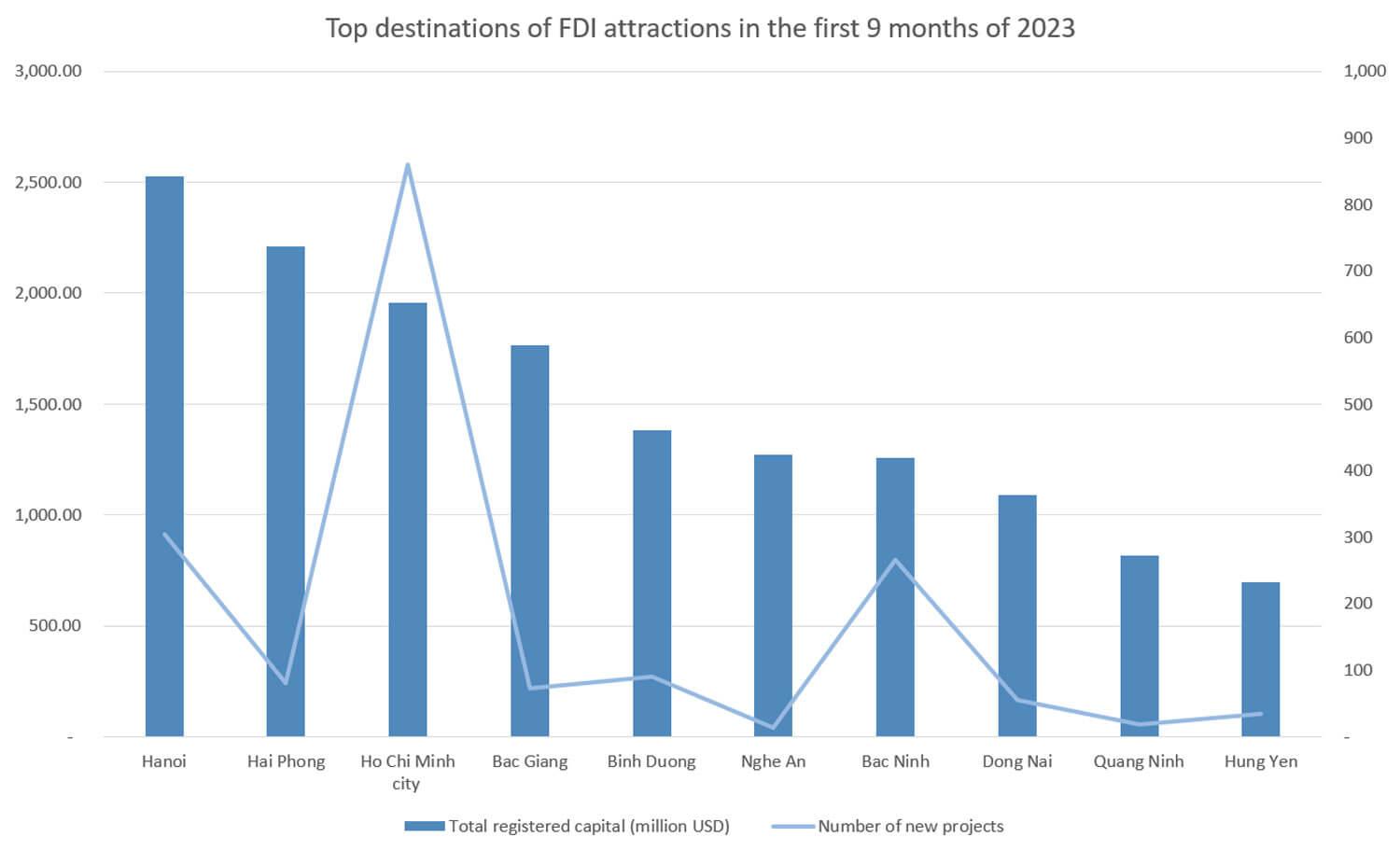
According to the Foreign Investment Department, the provinces and cities attracted the highest FDI in the first 9 months of 2023, as of September 20, Hanoi is leading with 2.53 billion USD. Hai Phong ranked second with a total registered capital of nearly 2.21 billion USD. Next, they are Ho Chi Minh City, Bac Giang, Binh Duong,…
Countries investing the most in Vietnam
For many years, Korea, Japan and Singapore have always led in the list of FDI sources in Vietnam. Big multinational corporations that have invested in Vietnam include Honda and Toyota (Japan); LG, Samsung (Korea); …
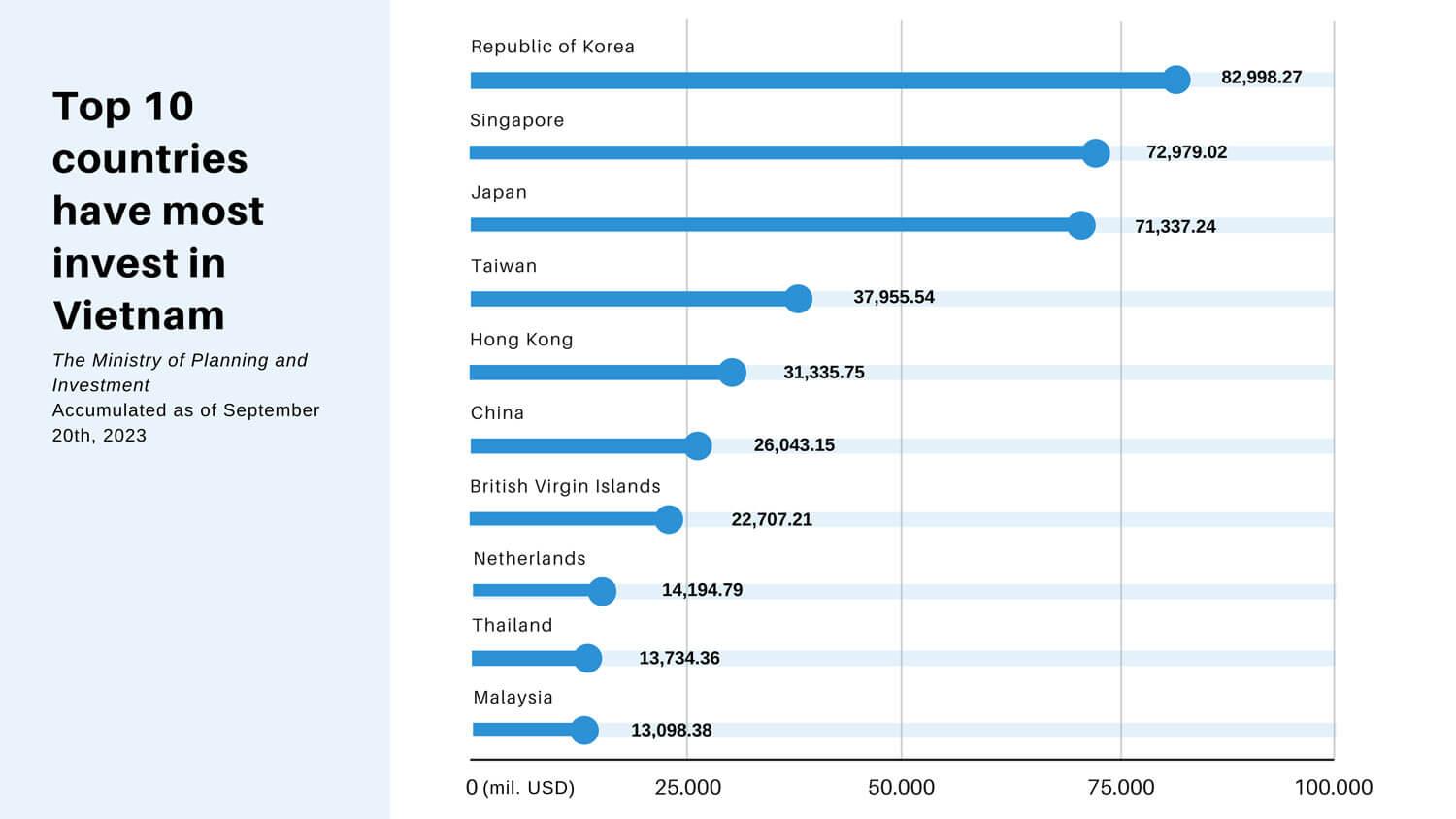
Leading partners in foreign investment in Vietnam
According to the Ministry of Planning and Investment, cumulatively by September 20, 2023, capital investment from Korea, Japan and Singapore has accounted for 50% of total foreign investment in Vietnam.
Industries attracting foreign investment in Vietnam
Foreign investors have invested in 18 out of 21 national economic sectors, in which the processing and manufacturing industry occupies the leading position in terms of foreign investment in Vietnam.
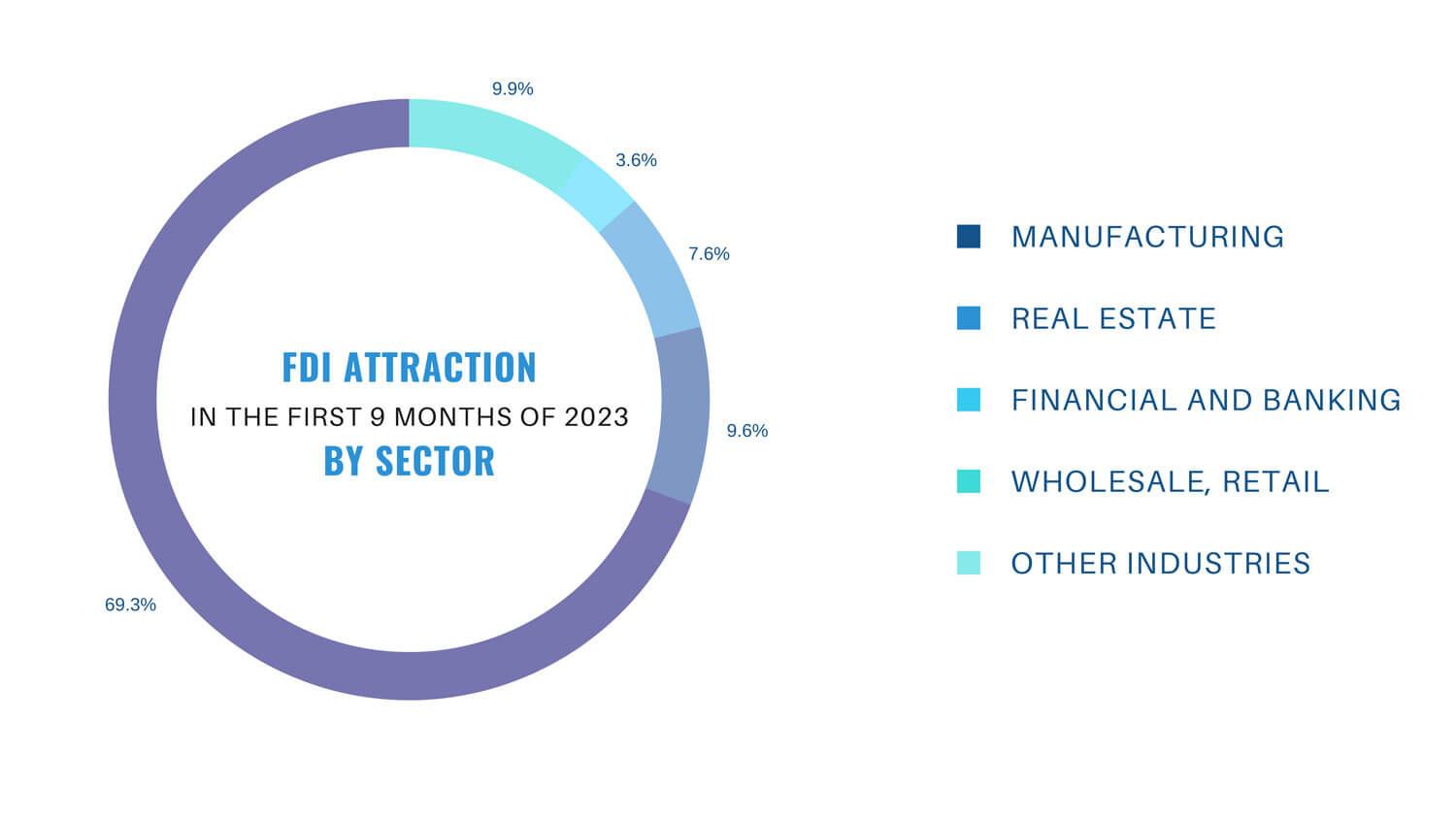
The leading industry group in attracting foreign investment in Vietnam
In the first 9 months of 2023, the processing and manufacturing industry has attracted more than 14 billion USD, accounting for nearly 69.3% of total registered investment and an increase of 15.5% in the same period. The real estate business ranked the second with total investment of nearly 1.94 billion USD, accounting for more than 9.6% of total registered investment. The banking and finance, wholesale and retail ranked the third and the fourth with total registered investment of nearly 1.54 billion USD and nearly 734 million USD, respectively.
What occupations are prohibited for foreign investors?
The Vietnamese Government stipulates that foreign investors are not allowed to invest in the following 25 sectors:
- Trading in goods and services on the list of state monopolies.
- Journalism and news gathering activities in all forms.
- Fishing or exploiting seafood.
- Investigation and security services.
- Judicial administrative services include judicial appraisal services, bailiff services, asset auction services, notary services, and administrator services.
- Services of sending workers to work abroad under contract.
- Investing in the construction of cemetery and graveyard infrastructure.
- Garbage collection service directly from households.
- Public opinion poll service (public opinion poll).
- Blasting service.
- Producing and trading in weapons, explosives and support tools.
- Importing and dismantling used ships.
- Public postal service.
- Business of border-gate transfer of goods.
- Trading in temporary imports for re-export activities.
- Import, export and distribution of goods on the List of goods of foreign investors and foreign-invested economic organizations are not allowed.
- Collecting, purchasing, and handling public assets at units of the armed forces.
- Production of military materials or equipment.
- Trading in industrial property representation services and intellectual property assessment services.
- Service of establishing, operating, maintaining marine signals; construction survey and publishing services of nautical charts of water areas, ports…
- Regulation services to ensure maritime safety in water areas, and public marine fairway; maritime electronic information services.
- Inspection and certification services for means of transport.
- Service of investigation, assessment and exploitation of natural forests.
- Researching or using genetic resources of new livestock breeds before being expertised by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
- Travel service business, except international travel services serving international tourists to Vietnam.
Source: Ministry of Planning and Investment, General Statistics Office, Tuoi Tre Newspaper, Industry and Trade Magazine
See more: Investment consultancy – project management
See more: The wave of attracting investment in the electronics industry in Vietnam






